Azithromycin For Cats Dosage Chart
Azithromycin For Cats Dosage Chart - Web veterinarians use azithromycin to treat a wide range of bacterial infections in dogs and cats including streptococci, staphylococci, bartonella henselae, some species of chlamydia, haemophilus spp, mycoplasma spp, borrelia burgdorferi, and others. Web azithromycin is an antibiotic sometimes used to treat bacterial infections in cats. Web the dosage will vary depending on the specific infection being treated, as well as your cat’s weight and overall health. It is essential to consult with your veterinarian to determine the proper dosage for your feline companion. Web for most infections, the standard adult dosage of azithromycin ranges from 500mg to 2000mg, taken once daily for 1 to 5 days. Your veterinarian may want you to use a tapering dose which means gradually decreasing how often you give the medication over a set period of time. The medication should be administered with or without food. Important considerations when administering azithromycin: In cats, the usual dosage is 2.5 to 7.5 mg per pound (5 to 15 mg/kg) orally every 12 to 24 hours for up to 7 days. Azithromycin is highly bioavailable after being administered per os (po) in dogs (97%), and only moderately bioavailable in cats (58%) and humans Web antibiotic dosing can vary a great deal depending on the antibiotic being used and the type of infection being treated. Po | iv oral (po) reference for this graph: Important considerations when administering azithromycin: In cats, the usual dosage is 2.5 to 7.5 mg per pound (5 to 15 mg/kg) orally every 12 to 24 hours for up to 7 days. Your veterinarian may want you to use a tapering dose which means gradually decreasing how often you give the medication over a set period of time. In cats, it is most common for the liquid oral suspension to be prescribed, as the available tablet sizes are too big for dosing in most cats. Web azithromycin for cats needs to be prescribed by a veterinarian. It is essential to consult with your veterinarian to determine the proper dosage for your feline companion. Web for most infections, the standard adult dosage of azithromycin ranges from 500mg to 2000mg, taken once daily for 1 to 5 days. The most common side effects of azithromycin in cats are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort. Azithromycin is available in various forms, including tablets, capsules, and liquid suspensions. Web discover the uses, dosing, and side effects of azithromycin for cats, an antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections in cats. Pediatric dosages are calculated based on the child's weight and are usually administered once daily for a specific number of days. In cats, it is most common. Azithromycin is highly bioavailable after being administered per os (po) in dogs (97%), and only moderately bioavailable in cats (58%) and humans Learn how it's used, side effects, and what to know if your cat is prescribed this medication. Not surprisingly, owner compliance can be poor resulting in apparent treatment failure. It is often combined with other drugs to treat. Web azithromycin for cats needs to be prescribed by a veterinarian. Web veterinarians use azithromycin to treat a wide range of bacterial infections in dogs and cats including streptococci, staphylococci, bartonella henselae, some species of chlamydia, haemophilus spp, mycoplasma spp, borrelia burgdorferi, and others. The medication should be administered with or without food. 8 mg/kg, sc, q 14 d, repeated. Pediatric dosages are calculated based on the child's weight and are usually administered once daily for a specific number of days. Treatment frequency and length can also vary quite a bit. Web discover the uses, dosing, and side effects of azithromycin for cats, an antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections in cats. The dosage for azithromycin can differ depending on. Web veterinarians use azithromycin to treat a wide range of bacterial infections in dogs and cats including streptococci, staphylococci, bartonella henselae, some species of chlamydia, haemophilus spp, mycoplasma spp, borrelia burgdorferi, and others. The dosage of zithromax® liquid 100mg /5ml (20 mg/ml) for felines is 0.25 ml/kg, and 200 mg/ml (40 mg/ml) is 0.125 ml/kg. In cats, the usual dosage. Web dose of azithromycin in dogs and cats. 10 milligrams per kilogram by mouth every 24 hours. It is often combined with other drugs to treat specific infections, such as atovaquone to treat babesiosis in dogs. Pediatric dosages are calculated based on the child's weight and are usually administered once daily for a specific number of days. Web for most. Your veterinarian may want you to use a tapering dose which means gradually decreasing how often you give the medication over a set period of time. Make sure to follow your veterinarian’s instructions carefully. Web the correct dose for the use of azithromycin in cats is 5 mg/kg (5 mg of drug for every 2.2 pounds of cat or 2.3. Web azithromycin for cats dosage. Treatment frequency and length can also vary quite a bit. Web discover the uses, dosing, and side effects of azithromycin for cats, an antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections in cats. The dosage for azithromycin can differ depending on the type of infection being treated. Web veterinarians use azithromycin to treat a wide range of. The recommended dosage for cats is 10 to 20 mg/kg orally every 24 hours or 5 to 10 mg/kg and is used to treat bacterial infections. 10 milligrams per kilogram by mouth every 24 hours. Pediatric dosages are calculated based on the child's weight and are usually administered once daily for a specific number of days. The medication should be. Important considerations when administering azithromycin: 20 mg/kg, po, q 24 h for a minimum of 3 weeks. Web the dosage will vary depending on the specific infection being treated, as well as your cat’s weight and overall health. The dosage for azithromycin can differ depending on the type of infection being treated. Make sure to follow your veterinarian’s instructions carefully. Important considerations when administering azithromycin: Azithromycin is highly bioavailable after being administered per os (po) in dogs (97%), and only moderately bioavailable in cats (58%) and humans The most common side effects of azithromycin in cats are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort. Do not give azithromycin to cats if the cat is allergic to azithromycin or similar drugs (macrolide. In cats, it is most common for the liquid oral suspension to be prescribed, as the available tablet sizes are too big for dosing in most cats. Treatment frequency and length can also vary quite a bit. In cats, the usual dosage is 2.5 to 7.5 mg per pound (5 to 15 mg/kg) orally every 12 to 24 hours for up to 7 days. Make sure to follow your veterinarian’s instructions carefully. Your veterinarian may want you to use a tapering dose which means gradually decreasing how often you give the medication over a set period of time. Web the dosage will vary depending on the specific infection being treated, as well as your cat’s weight and overall health. Pediatric dosages are calculated based on the child's weight and are usually administered once daily for a specific number of days. Not surprisingly, owner compliance can be poor resulting in apparent treatment failure. Learn how it's used, side effects, and what to know if your cat is prescribed this medication. Web available as 250 mg, 500 mg, 600 mg tablets, and oral suspension (liquid) background. Web the correct dose for the use of azithromycin in cats is 5 mg/kg (5 mg of drug for every 2.2 pounds of cat or 2.3 mg per pound of cat). Web azithromycin is an antibiotic sometimes used to treat bacterial infections in cats.AZITHROMYCIN
Azithromycin in Cats Antimicrobials
Guide About Azithromycin Dosage For Cats & Chart By Weight
Treatment of Feline Lower Airway Disease Today's Veterinary Practice
Azithromycin Dosage Chart For Cats
Azithromycin in Cats Antimicrobials
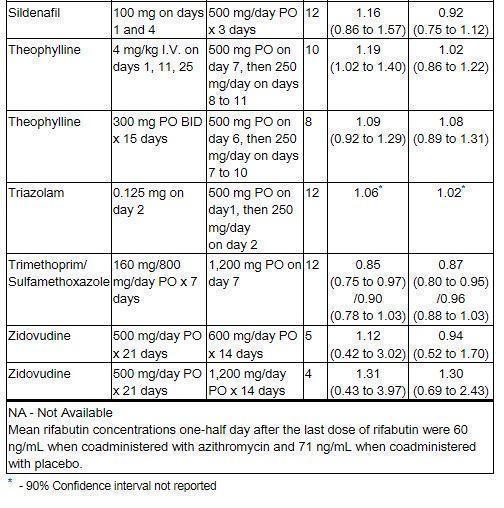
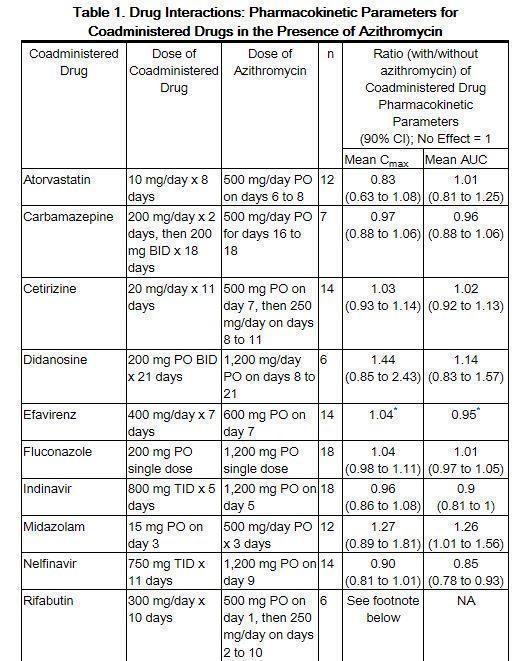
AZITHROMYCIN
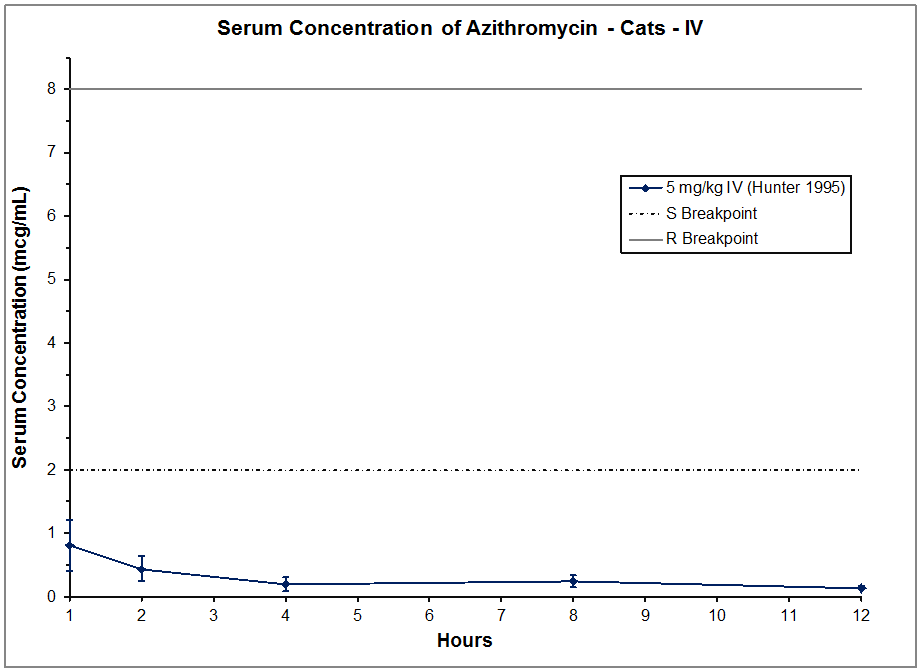
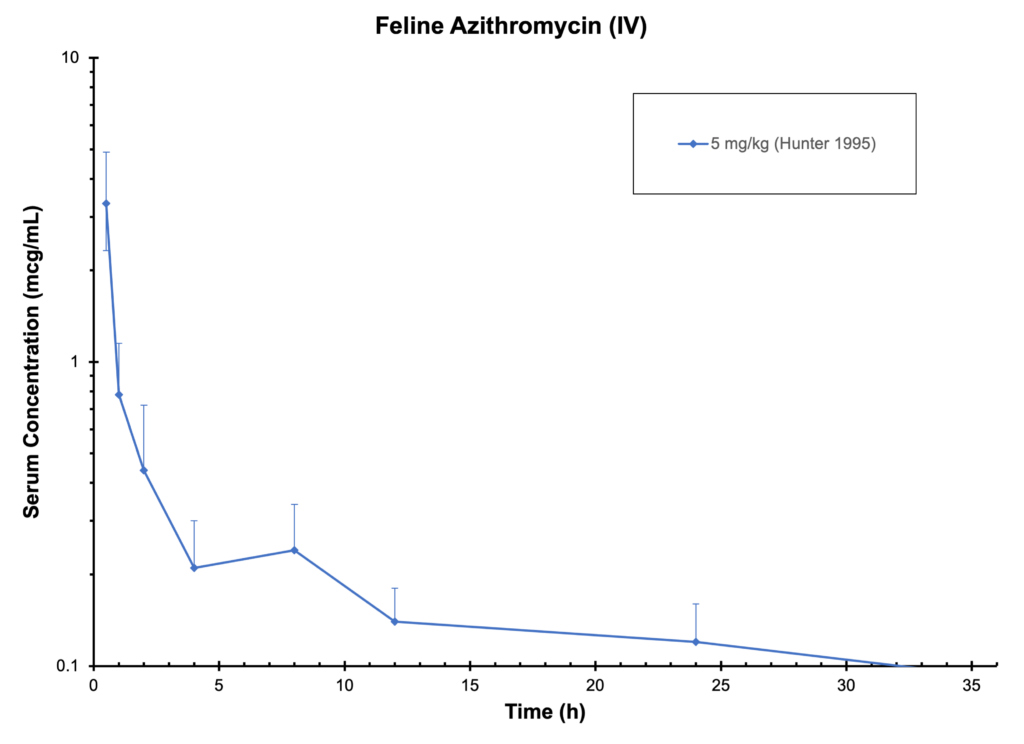
CAT AZITHROMYCIN (IV) Antimicrobials
Azithromycin Dosage For Cats
Azithromycin For Cats Dosage Chart Cat Meme Stock Pictures and Photos
It Is Often Combined With Other Drugs To Treat Specific Infections, Such As Atovaquone To Treat Babesiosis In Dogs.
8 Mg/Kg, Sc, Q 14 D, Repeated As Needed If Response To Therapy Is Not Complete (Maximum Treatment Should Not Exceed 2 Injections) A.
The Medication Should Be Administered With Or Without Food.
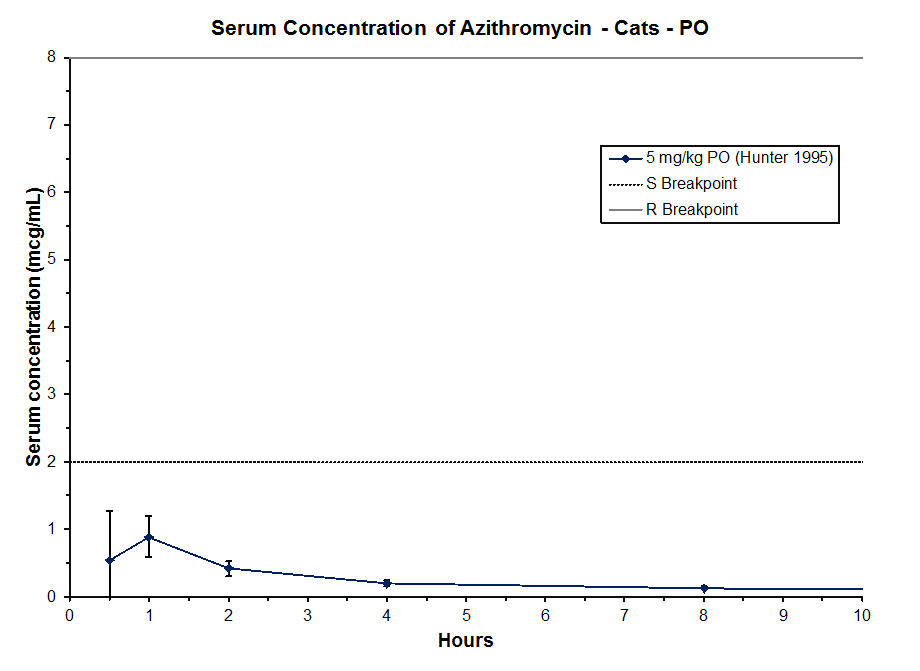
Hunter 1995 Intravenous (Iv) Reference For This Graph:
Related Post: