Chemical Nomenclature Chart
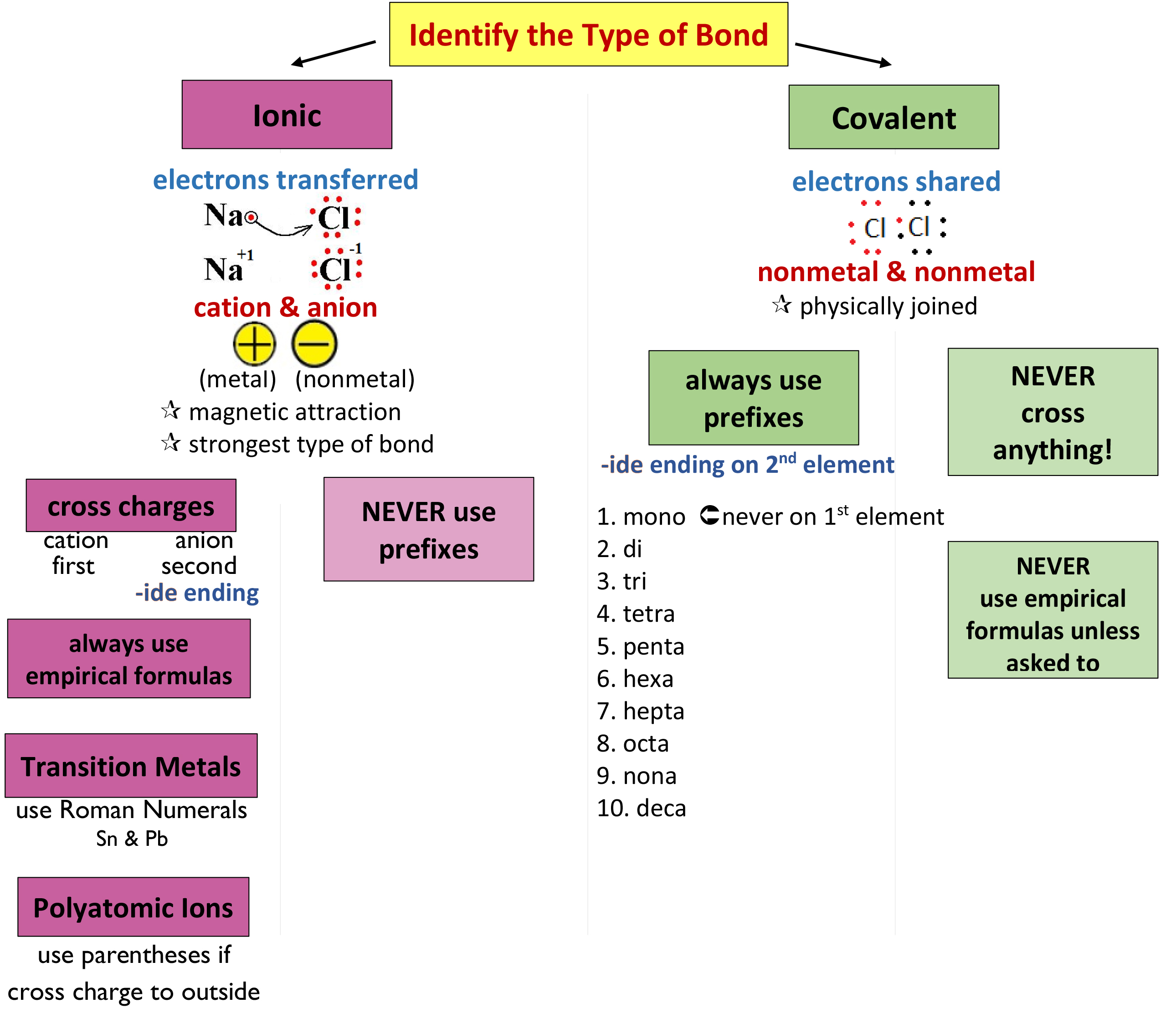
Chemical Nomenclature Chart - To summarize, many compounds may be classified into five different categories, each of which uses a slightly different, but related, set of rules. Web chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds. For naming purposes, a chemical compound is treated as a combination of a parent compound (section 5) and characteristic (functional) groups, one of which is Web derive names for common types of inorganic compounds using a systematic approach. It is published in the nomenclature of organic chemistry (informally called the blue book ). If only one atom of a specific type is present, no subscript is used. The rules we use depends on the type of compound we are attempting to name. By the end of this section, you will be able to: The rules we use in nomenclature depend on the types of bonds the compound has and these are outlined in figure 2.7.1 2.7. Web the following website provides practice with naming chemical compounds and writing chemical formulas. The rules we use in nomenclature depend on the types of bonds the compound has and these are outlined in figure 2.7.1 2.7. To summarize, many compounds may be classified into five different categories, each of which uses a slightly different, but related, set of rules. In this section, we discuss. Web chemical nomenclature | introduction to chemistry. Web learn the basic rules and principles of nomenclature for organic and inorganic compounds, according to the iupac standards. This module describes an approach that is used to name simple ionic and molecular compounds, such as nacl, caco 3, and n 2 o 4. These five common classes of compounds are. Web the basics of organic nomenclature, of inorganic nomenclature and polymer nomenclature are summarized in a collection of brief guides accessible below. Web iupac nomenclature is used for the naming of chemical compounds, based on their chemical composition and their structure. For atoms that have two or more present, a subscript. Web chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds. Names that are arbitrary (including the names of the elements, such as sodium and hydrogen) as well as laboratory shorthand names (such as diphos and lithal) are Web the system used for naming chemical substances depends on the nature of the molecular units making up. Web the following website provides practice with naming chemical compounds and writing chemical formulas. Chemists use specific rules and conventions to name different compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the international union of pure and applied chemistry (iupac). Web specialists in nomenclature recognise two different categories of nomenclature. Binary compound (metal/nonmetal) with. It is published in the nomenclature of organic chemistry (informally called the blue book ). Web in this section we will look at nomenclature of simple chemical compounds. These compilations are coordinated by the division of chemical nomenclature and. You can choose binary, polyatomic, and variable charge ionic compounds, as well as molecular compounds. Chemists use specific rules and conventions. Web nomenclature, a collection of rules for naming things, is important in science and in many other situations. Chemical nomenclature is the term given to the naming of compounds. Iupac is best known for its works standardizing nomenclature in chemistry and other fields of science. Web iupac nomenclature is used for the naming of chemical compounds, based on their chemical. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the international union of pure and applied chemistry (iupac). Web iupac nomenclature is used for the naming of chemical compounds, based on their chemical composition and their structure. Web tutorials and problem sets. For atoms that have two or more present, a subscript. Names that are arbitrary. Web the system used for naming chemical substances depends on the nature of the molecular units making up the compound. You can choose binary, polyatomic, and variable charge ionic compounds, as well as molecular compounds. It is published in the nomenclature of organic chemistry (informally called the blue book ). Derive names for common types of inorganic compounds using a. In this section, we discuss. Nomenclature, a collection of rules for naming things, is important in science and in many other situations. Binary compound (metal/nonmetal) with variable charge cation: Chemical nomenclature is the term given to the naming of compounds. Web in chemical nomenclature, the iupac nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic chemical compounds as recommended. It is published in the nomenclature of organic chemistry (informally called the blue book ). Chemists use specific rules and conventions to name different compounds. Different rules apply to each. Nomenclature, a collection of rules for naming things, is important in science and in many other situations. These are usually either ions or molecules; In this section, we discuss. Iupac is best known for its works standardizing nomenclature in chemistry and other fields of science. Web the system used for naming chemical substances depends on the nature of the molecular units making up the compound. Web in chemical nomenclature, the iupac nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic chemical compounds as. The rules we use in nomenclature depend on the types of bonds the compound has and these are outlined in figure 2.7.1 2.7. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Web chemical nomenclature | introduction to chemistry. For atoms that have two or more present, a subscript. Web in this section we will look at nomenclature. These are usually either ions or molecules; For naming purposes, a chemical compound is treated as a combination of a parent compound (section 5) and characteristic (functional) groups, one of which is For atoms that have two or more present, a subscript. Web the full text of iupac and iubmb organic and biochemical nomenclature recommendations. Web chemical nomenclature | introduction to chemistry. Web in chemical nomenclature, the iupac nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic chemical compounds as recommended [1] [2] by the international union of pure and applied chemistry (iupac). Nomenclature, a collection of rules for naming things, is important in science and in many other situations. Web learn the basic rules and principles of nomenclature for organic and inorganic compounds, according to the iupac standards. Today we often use chemical formulas, such as nacl, c 12 h 22 o 11, and co (nh 3) 6 (clo 4) 3 , to describe chemical compounds. Nomenclature, a collection of rules for naming things, is important in science and in many other situations. If only one atom of a specific type is present, no subscript is used. The goal of the system is to provide each organic compound with a unique and unambiguous name based on its chemical formula and structure. Web nomenclature, a collection of rules for naming things, is important in science and in many other situations. The rules we use depends on the type of compound we are attempting to name. You can choose binary, polyatomic, and variable charge ionic compounds, as well as molecular compounds. Binary compound (metal/nonmetal) with fixed charge cation.Chemistry Nomenclature Chart
Chemical Nomenclature and Chemical Formulas Owlcation
Organic Chemistry Nomenclature Chart
07 Nomenclature Mrs. Cook's Chemistry Class
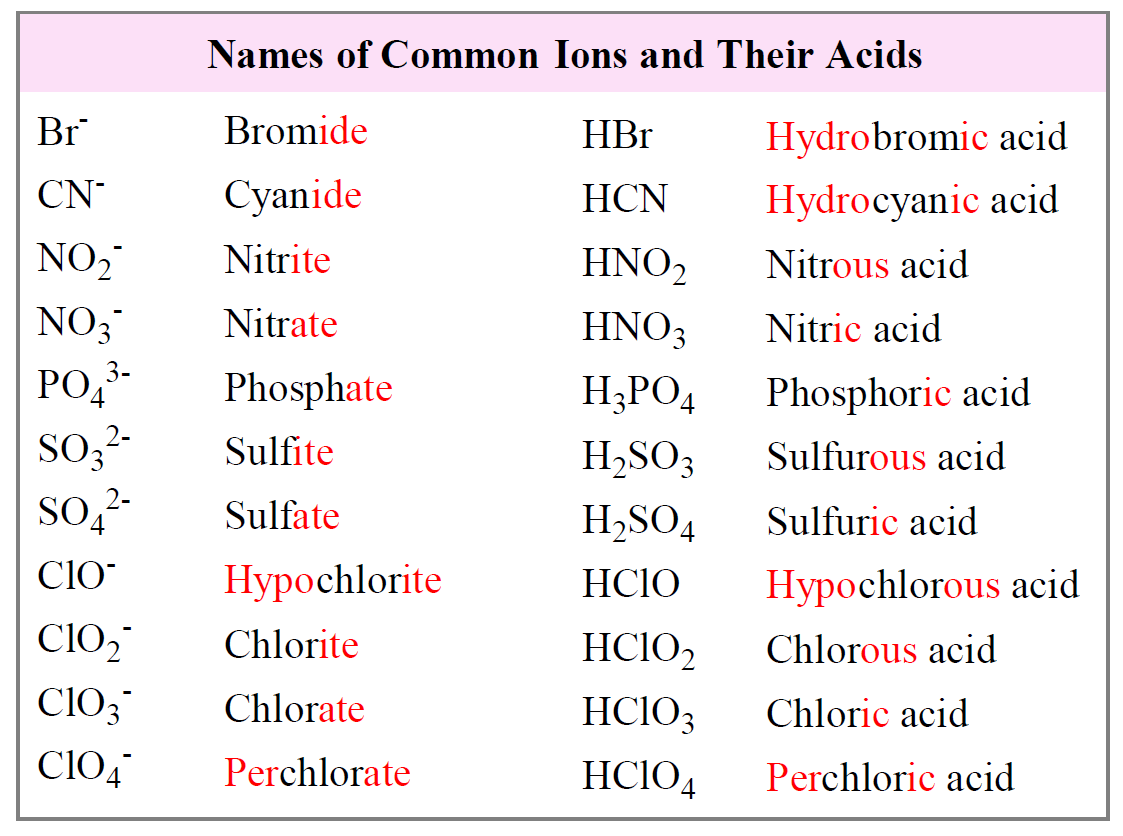
Naming Acids and Bases Chemistry Steps
CPSC Organic Chemistry Nomenclature
Chemistry Nomenclature Chart
Chemistry Nomenclature Chart
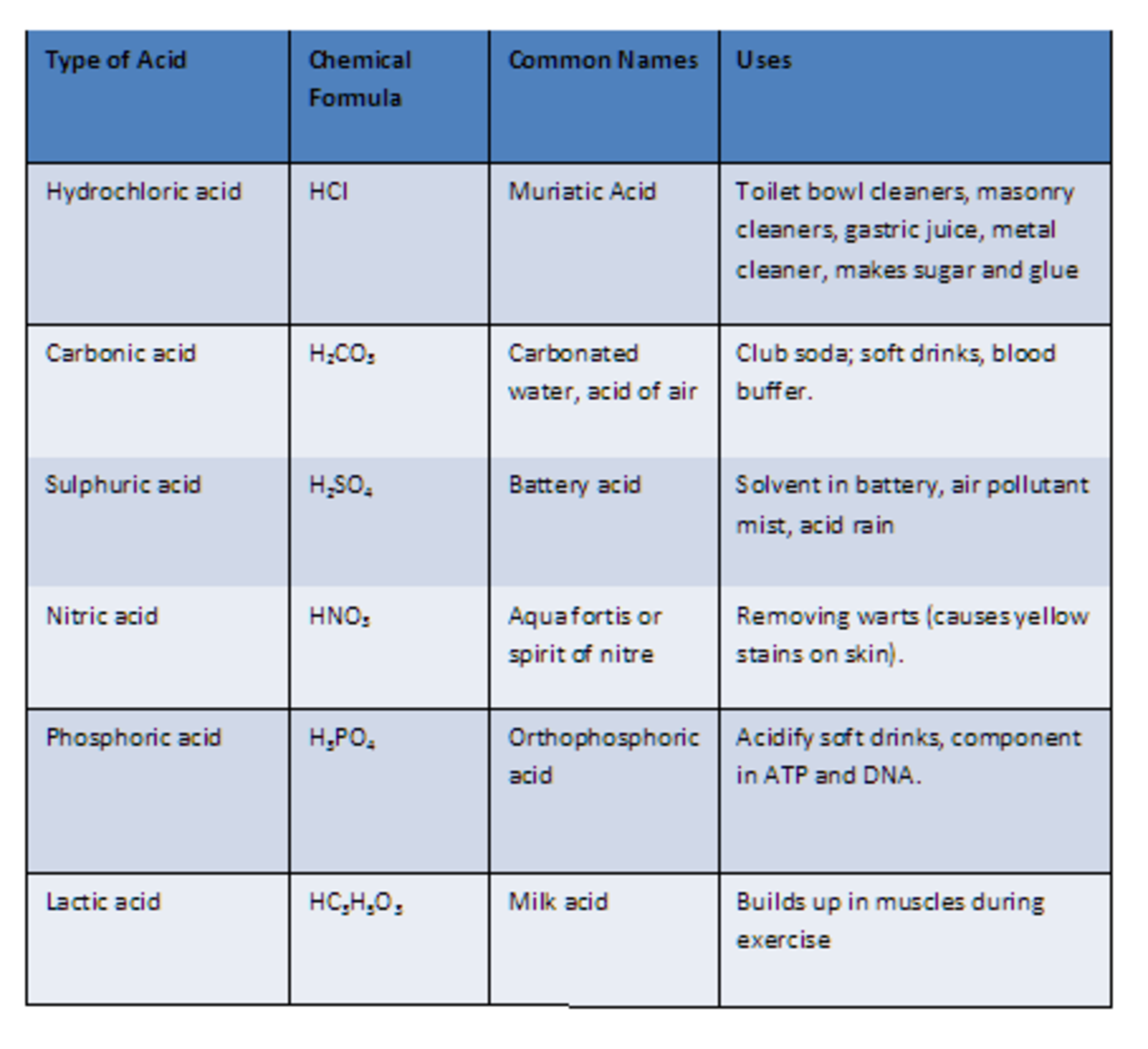
Nomenclature of Acids Pathways to Chemistry
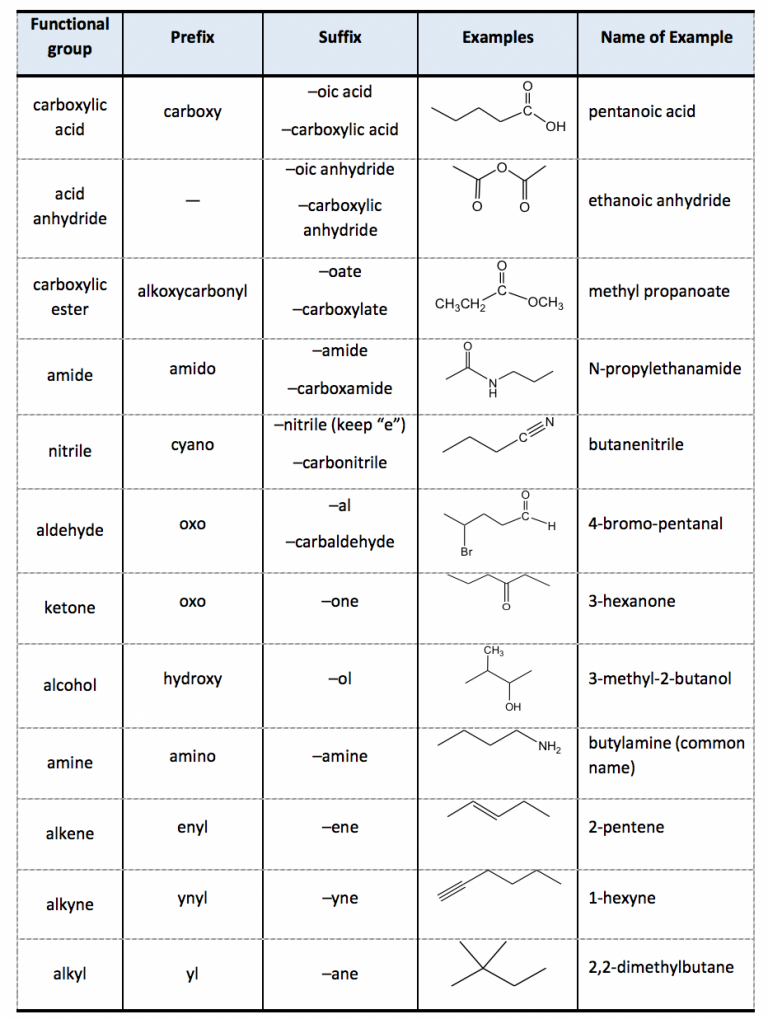
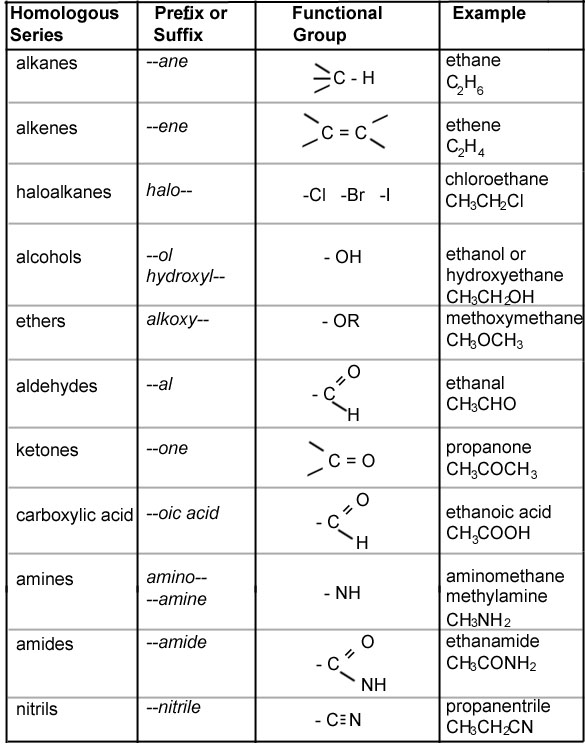
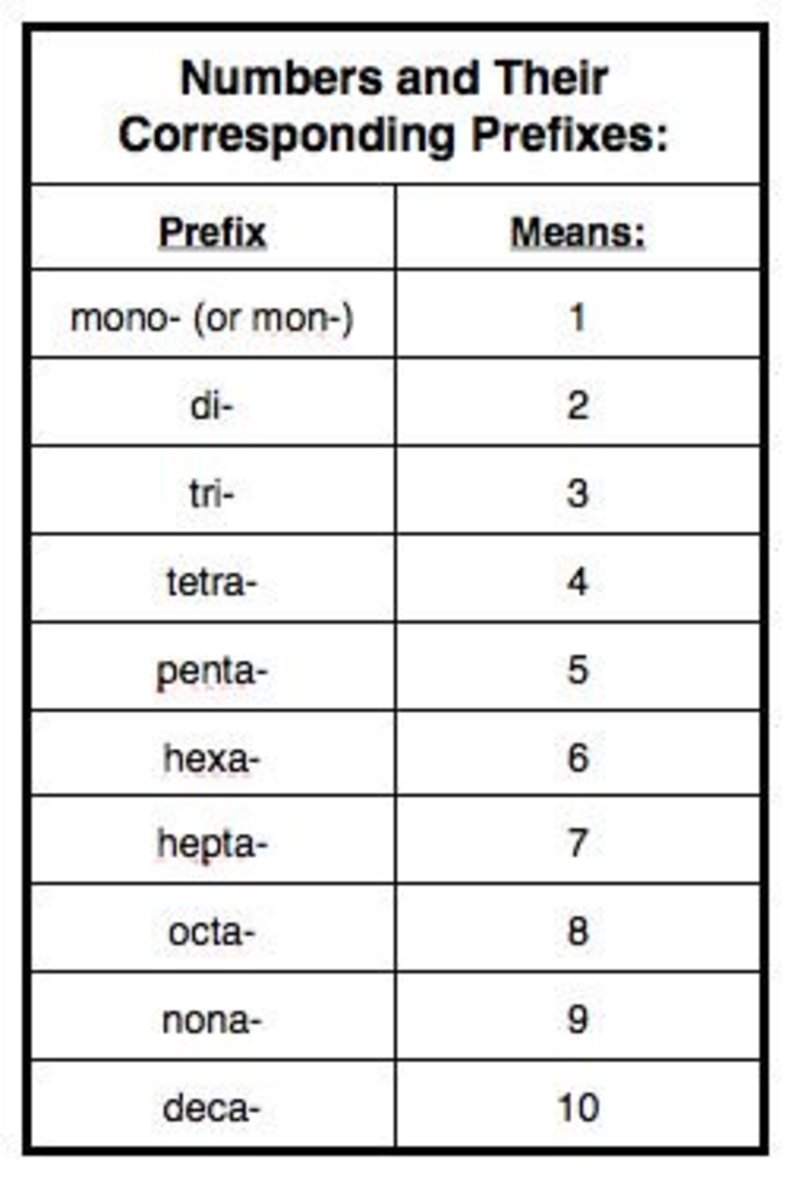
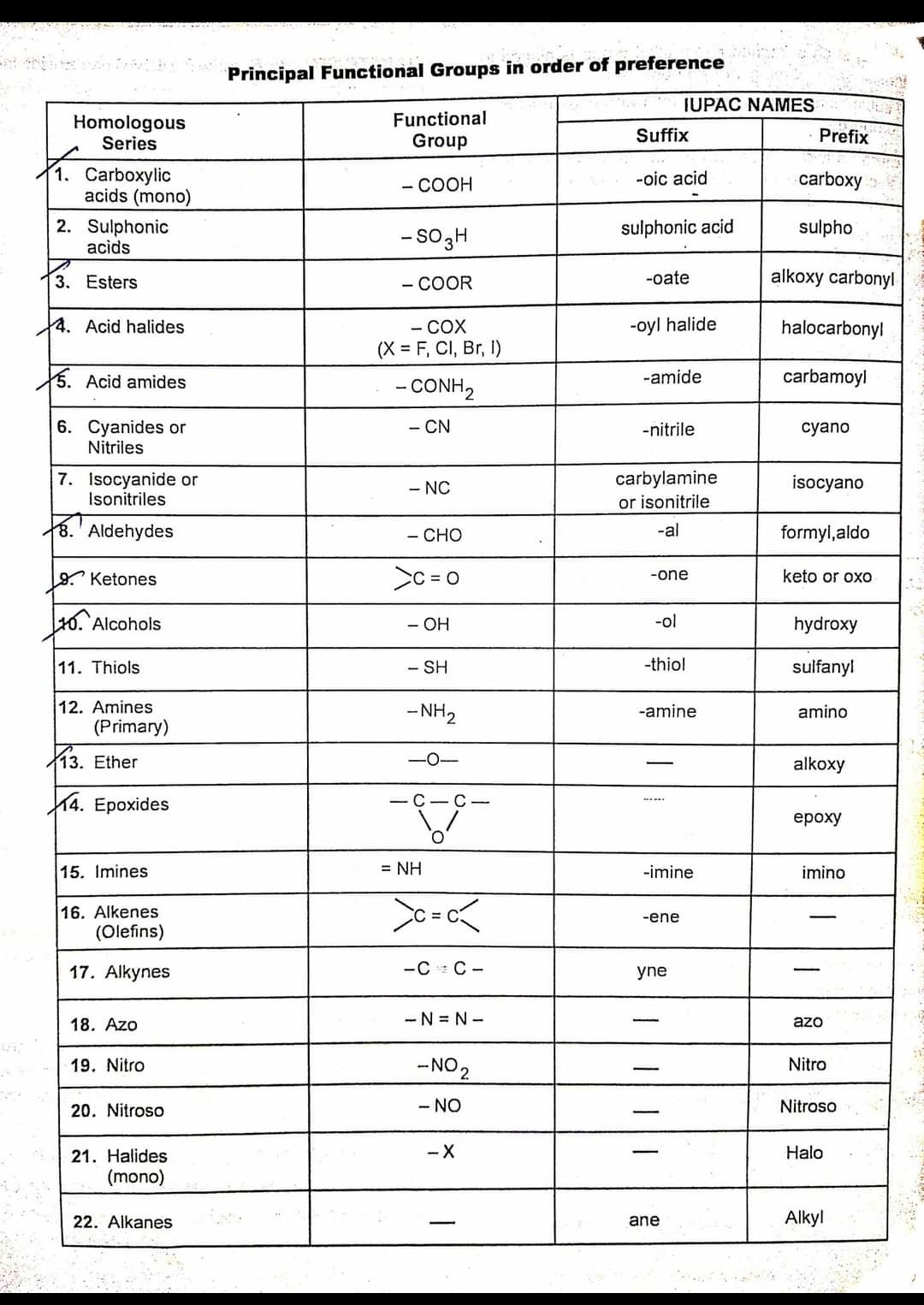
IUPAC Chart Functional Group And Suffix Prefix And Their Principal
Web Tutorials And Problem Sets.
Chemists Use Specific Rules And Conventions To Name Different Compounds.
Chemical Nomenclature Is The Term Given To The Naming Of Compounds.
A Molecular Formula Tells Us What Atoms And How Many Of Each Type Of Atom Are Present In A Molecule.
Related Post: