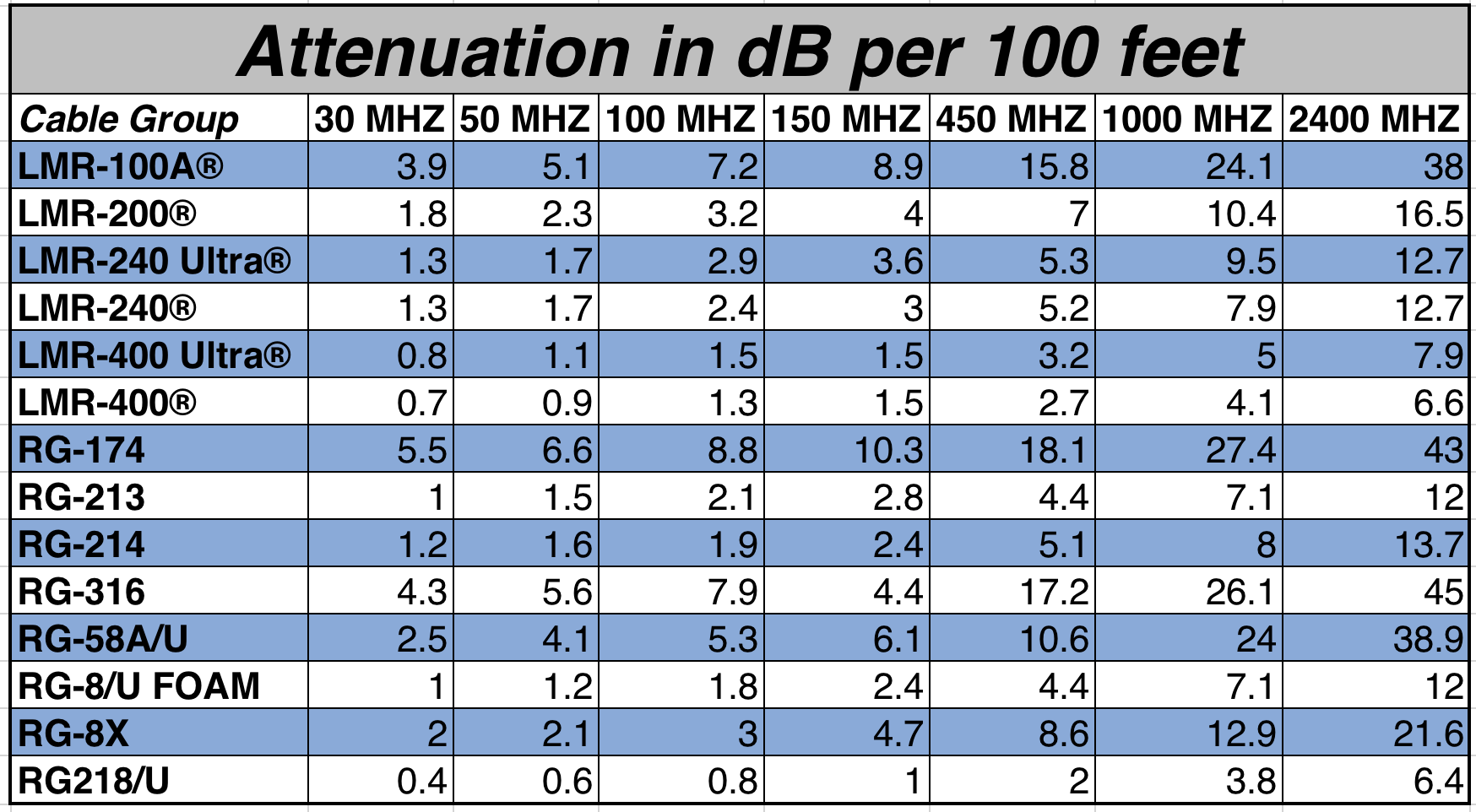
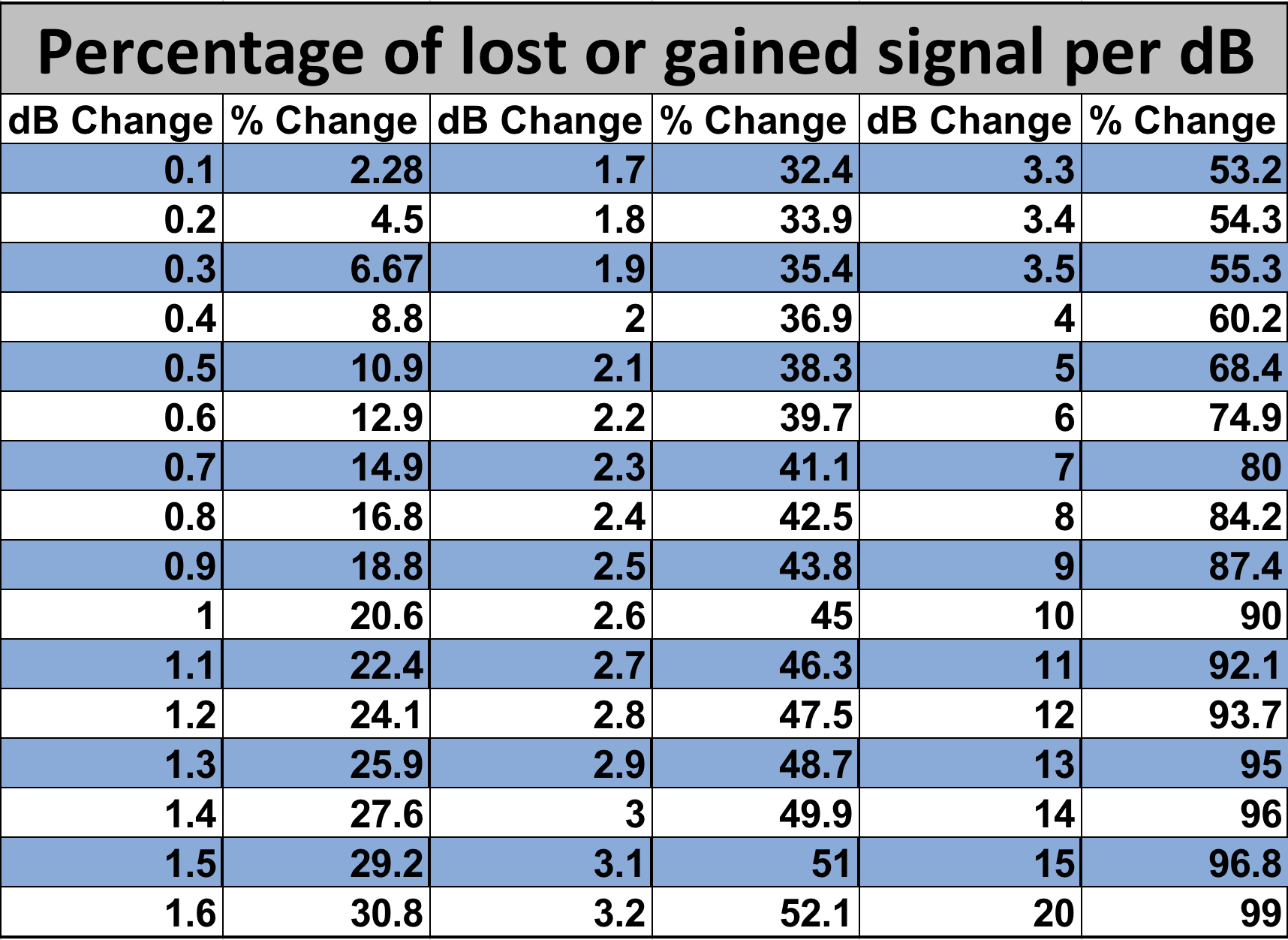
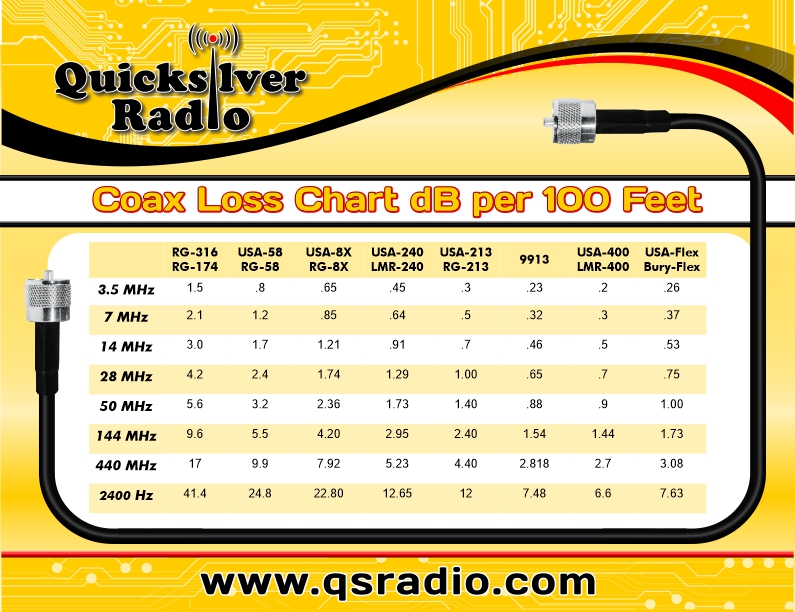
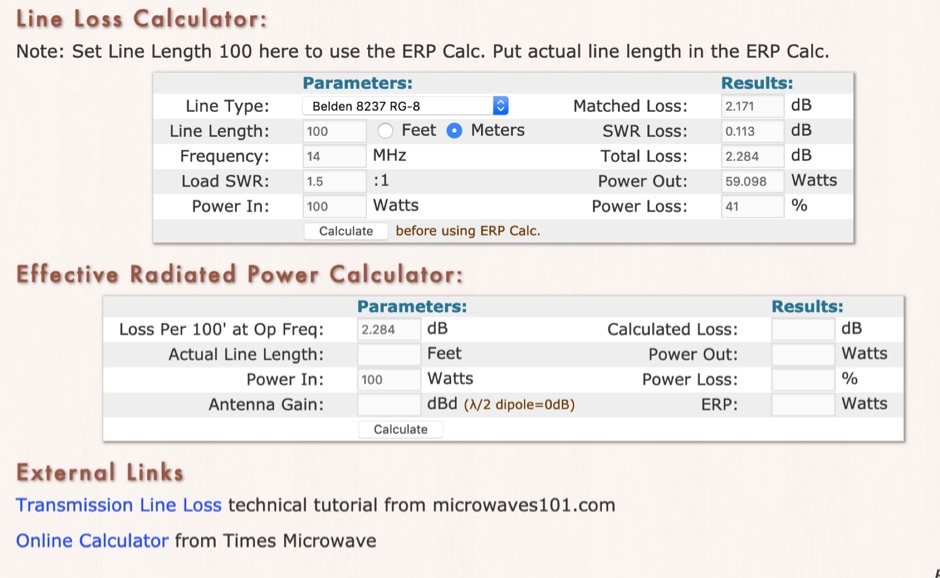
Coax Loss Chart
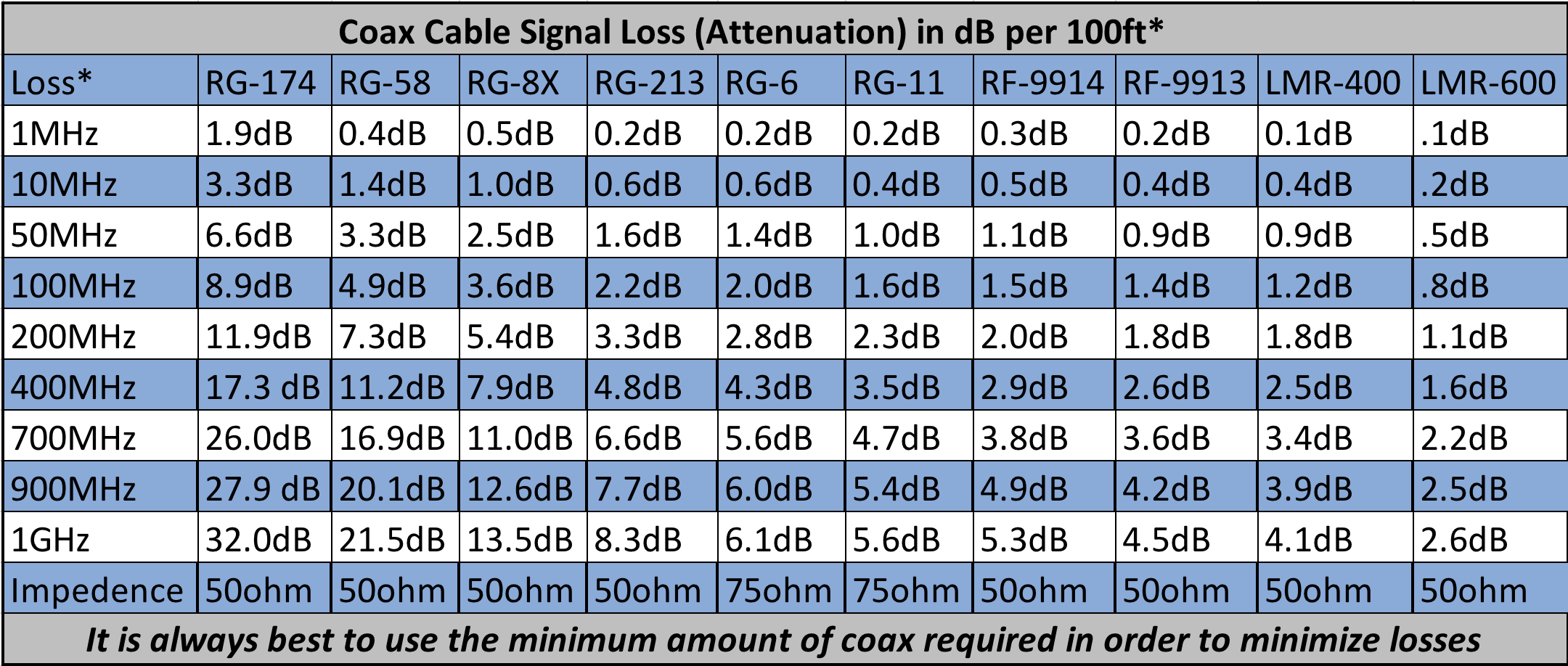
Coax Loss Chart - Here's a quick line loss calculator to use note that the simple program used for this web page gives a very close approximation for additional losses due to swr. Web coax cable signal loss (attenuation) in db per 100ft*. Understanding coaxial cable loss is essential for optimizing signal transmission and ensuring efficient communication systems. Inner conductor temperature 100°c (212°f); Average power rating, kw standard conditions: Web suitable for higher power (~1800 watts) at hf. Suitable for vhf (~1.5db loss per 100 feet at 146 mhz). Online coax cable loss / antenna gain calculator. Enter length of cable in feet. Choose from a variety of cables and get started now! Enter db loss of cable per 100 ft. Attenuation, db/100 ft (db/100 m) standard conditions: Inner conductor temperature 100°c (212°f); Suitable for vhf (~1.5db loss per 100 feet at 146 mhz). Average power rating, kw standard conditions: Understanding coaxial cable loss is essential for optimizing signal transmission and ensuring efficient communication systems. Loss is a length multiplier, so a 200 ft length would have twice the loss shown above and a 50 ft length would have half the loss. Coax losses shown above are for 100 feet lengths. Enter length of cable in feet. Here's a quick line loss calculator to use note that the simple program used for this web page gives a very close approximation for additional losses due to swr. Online coax cable loss / antenna gain calculator. Understanding coaxial cable loss is essential for optimizing signal transmission and ensuring efficient communication systems. Coax losses shown above are for 100 feet lengths. Loss is a length multiplier, so a 200 ft length would have twice the loss shown above and a 50 ft length would have half the loss. Enter. Inner conductor temperature 100°c (212°f); At the desired operating frequency. Understanding coaxial cable loss is essential for optimizing signal transmission and ensuring efficient communication systems. Here's a quick line loss calculator to use note that the simple program used for this web page gives a very close approximation for additional losses due to swr. Web coax cable signal loss (attenuation). Web attenuation (db per 100 feet): Average power rating, kw standard conditions: Enter db loss of cable per 100 ft. Suitable for vhf (~1.5db loss per 100 feet at 146 mhz). Attenuation, db/100 ft (db/100 m) standard conditions: Inner conductor temperature 100°c (212°f); Enter length of cable in feet. Choose from a variety of cables and get started now! Suitable for vhf (~1.5db loss per 100 feet at 146 mhz). At the desired operating frequency. Suitable for vhf (~1.5db loss per 100 feet at 146 mhz). Enter length of cable in feet. Loss is a length multiplier, so a 200 ft length would have twice the loss shown above and a 50 ft length would have half the loss. Attenuation, db/100 ft (db/100 m) standard conditions: Web attenuation (db per 100 feet): At the desired operating frequency. Attenuation, db/100 ft (db/100 m) standard conditions: Web attenuation (db per 100 feet): Online coax cable loss / antenna gain calculator. Understanding coaxial cable loss is essential for optimizing signal transmission and ensuring efficient communication systems. Average power rating, kw standard conditions: Web suitable for higher power (~1800 watts) at hf. Enter db loss of cable per 100 ft. Suitable for vhf (~1.5db loss per 100 feet at 146 mhz). Web calculate the attenuation and power handling capability of coaxial cables using the online calculator by times microwave systems. Coax losses shown above are for 100 feet lengths. Online coax cable loss / antenna gain calculator. Average power rating, kw standard conditions: Enter db loss of cable per 100 ft. Web calculate the attenuation and power handling capability of coaxial cables using the online calculator by times microwave systems. Web calculate the attenuation and power handling capability of coaxial cables using the online calculator by times microwave systems. Choose from a variety of cables and get started now! Online coax cable loss / antenna gain calculator. Enter db loss of cable per 100 ft. Attenuation, db/100 ft (db/100 m) standard conditions: Web calculate the attenuation and power handling capability of coaxial cables using the online calculator by times microwave systems. Web attenuation (db per 100 feet): Understanding coaxial cable loss is essential for optimizing signal transmission and ensuring efficient communication systems. Inner conductor temperature 100°c (212°f); Attenuation, db/100 ft (db/100 m) standard conditions: Web calculate the attenuation and power handling capability of coaxial cables using the online calculator by times microwave systems. Web coax cable signal loss (attenuation) in db per 100ft*. Coax losses shown above are for 100 feet lengths. Web attenuation (db per 100 feet): Suitable for vhf (~1.5db loss per 100 feet at 146 mhz). Loss is a length multiplier, so a 200 ft length would have twice the loss shown above and a 50 ft length would have half the loss. Web suitable for higher power (~1800 watts) at hf. Here's a quick line loss calculator to use note that the simple program used for this web page gives a very close approximation for additional losses due to swr. Enter db loss of cable per 100 ft. Online coax cable loss / antenna gain calculator. Attenuation, db/100 ft (db/100 m) standard conditions: Inner conductor temperature 100°c (212°f); Understanding coaxial cable loss is essential for optimizing signal transmission and ensuring efficient communication systems.Coax Loss and db loss chart The WIN System
Coax Cable Loss Chart
Ham Radio Coax Cable Loss Chart
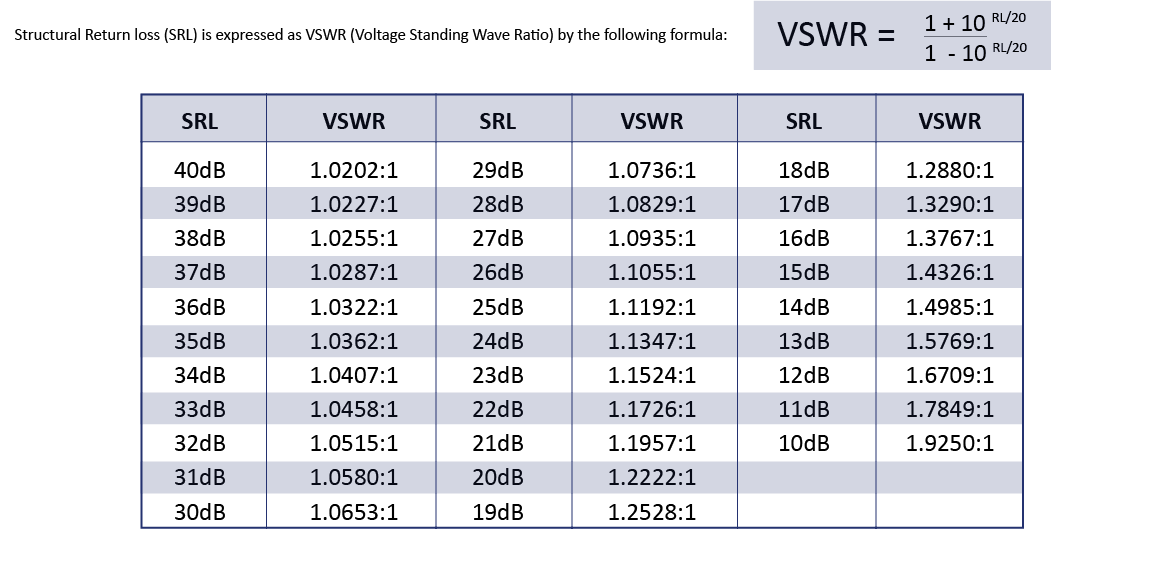
VSWR and Return Loss of Coaxial Cables
Coax Loss and db loss chart The WIN System
Coax Loss and db loss chart The WIN System
MEGA Information Thread for New HAM's Page 1
Coax Loss Calculator Online by K5VR Resource Detail
Coax Loss Measurements
Coax Attenuation Chart
Choose From A Variety Of Cables And Get Started Now!
Enter Length Of Cable In Feet.
Average Power Rating, Kw Standard Conditions:
At The Desired Operating Frequency.
Related Post: