Dental X Ray Radiation Dose Chart
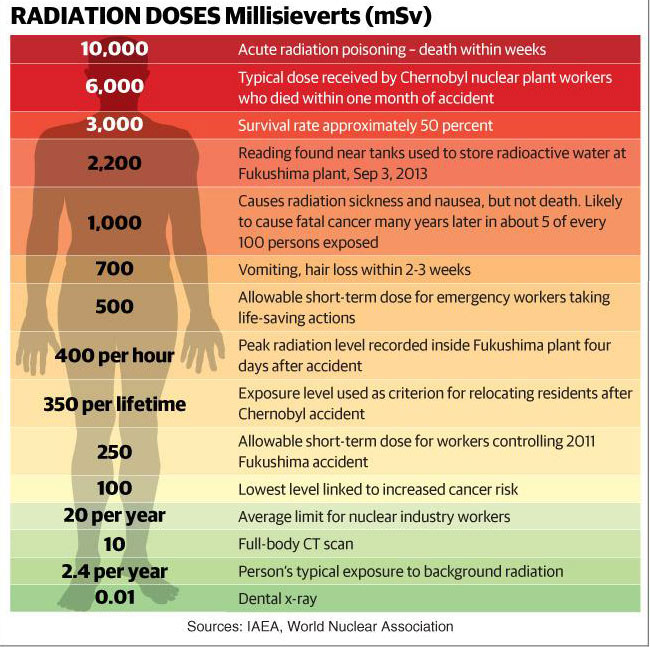
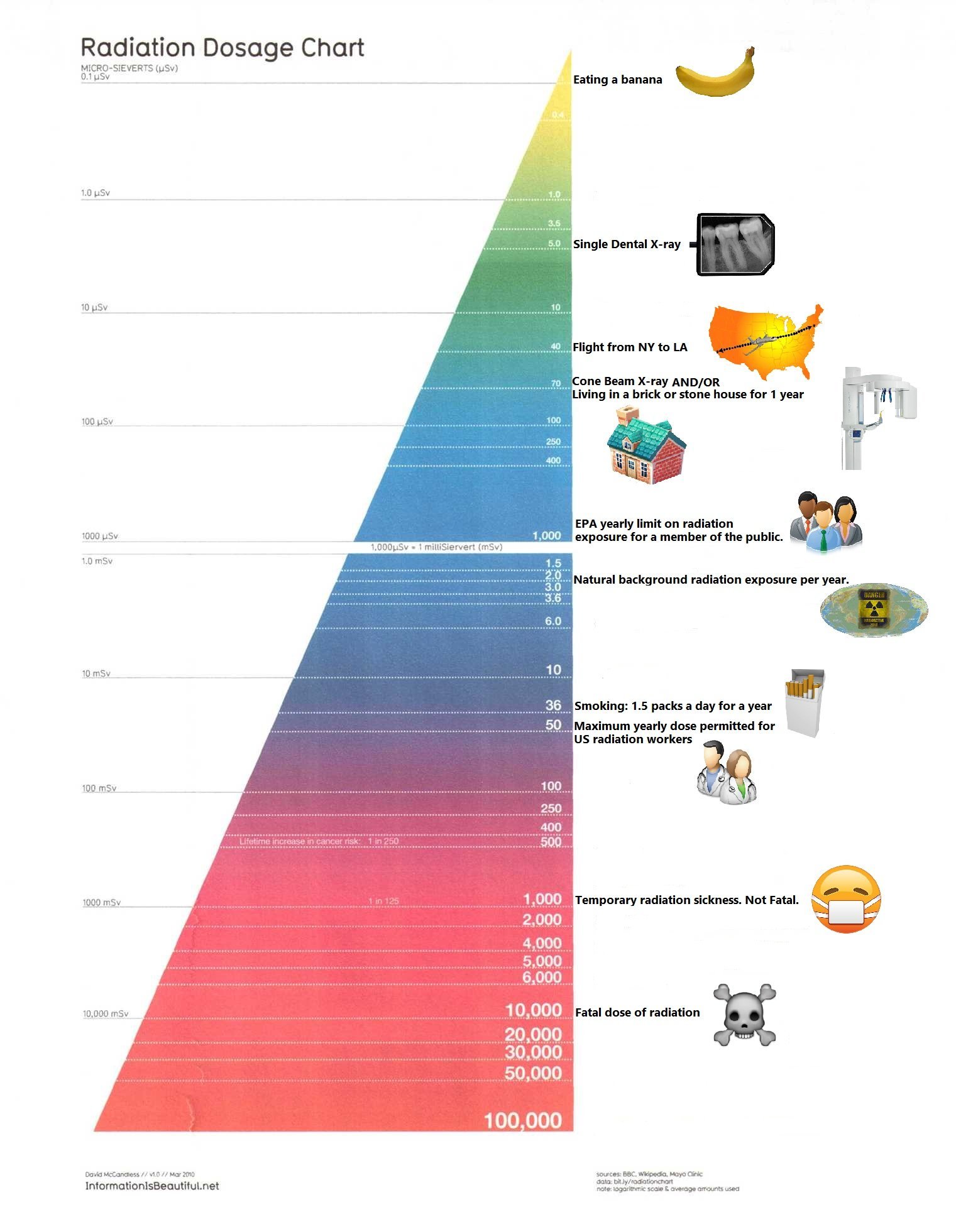
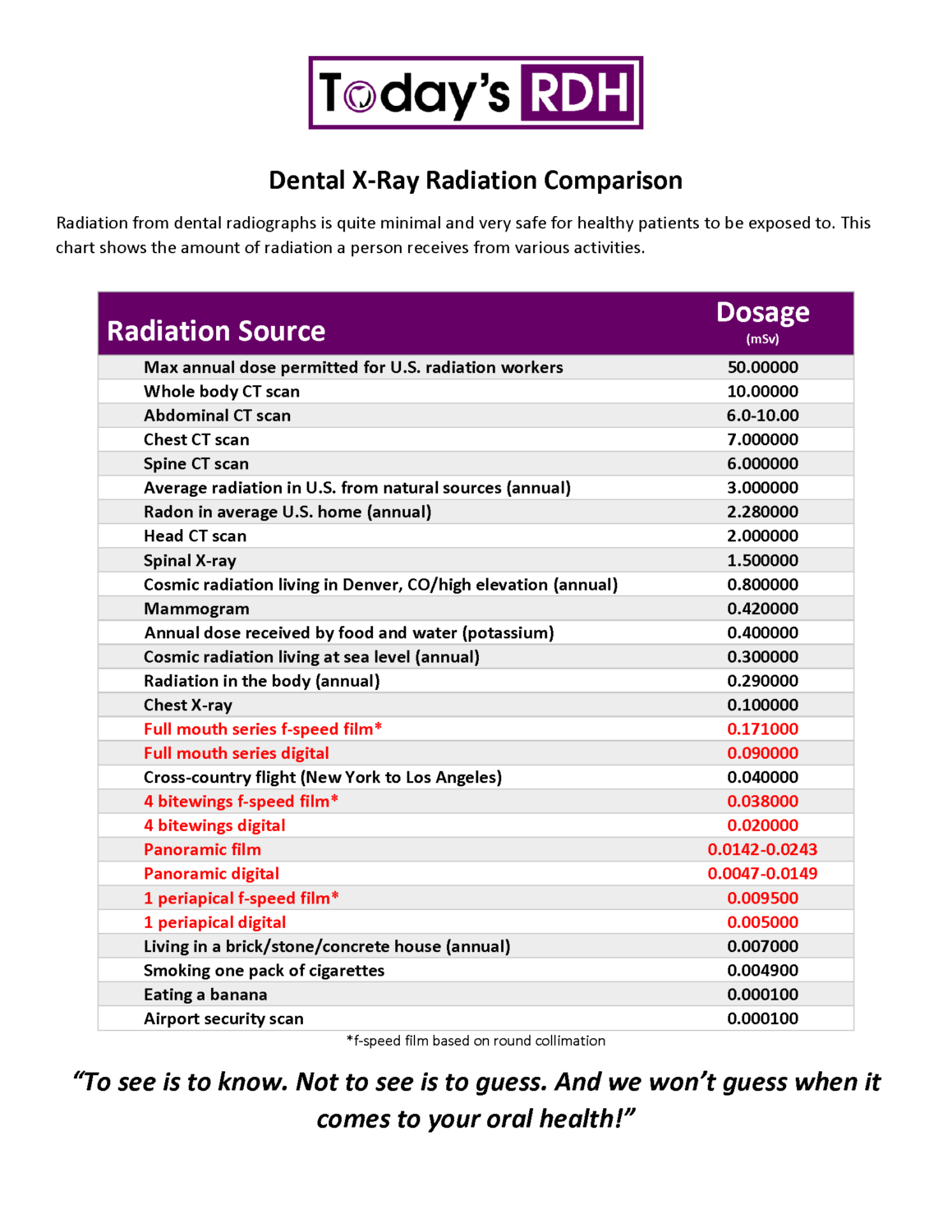
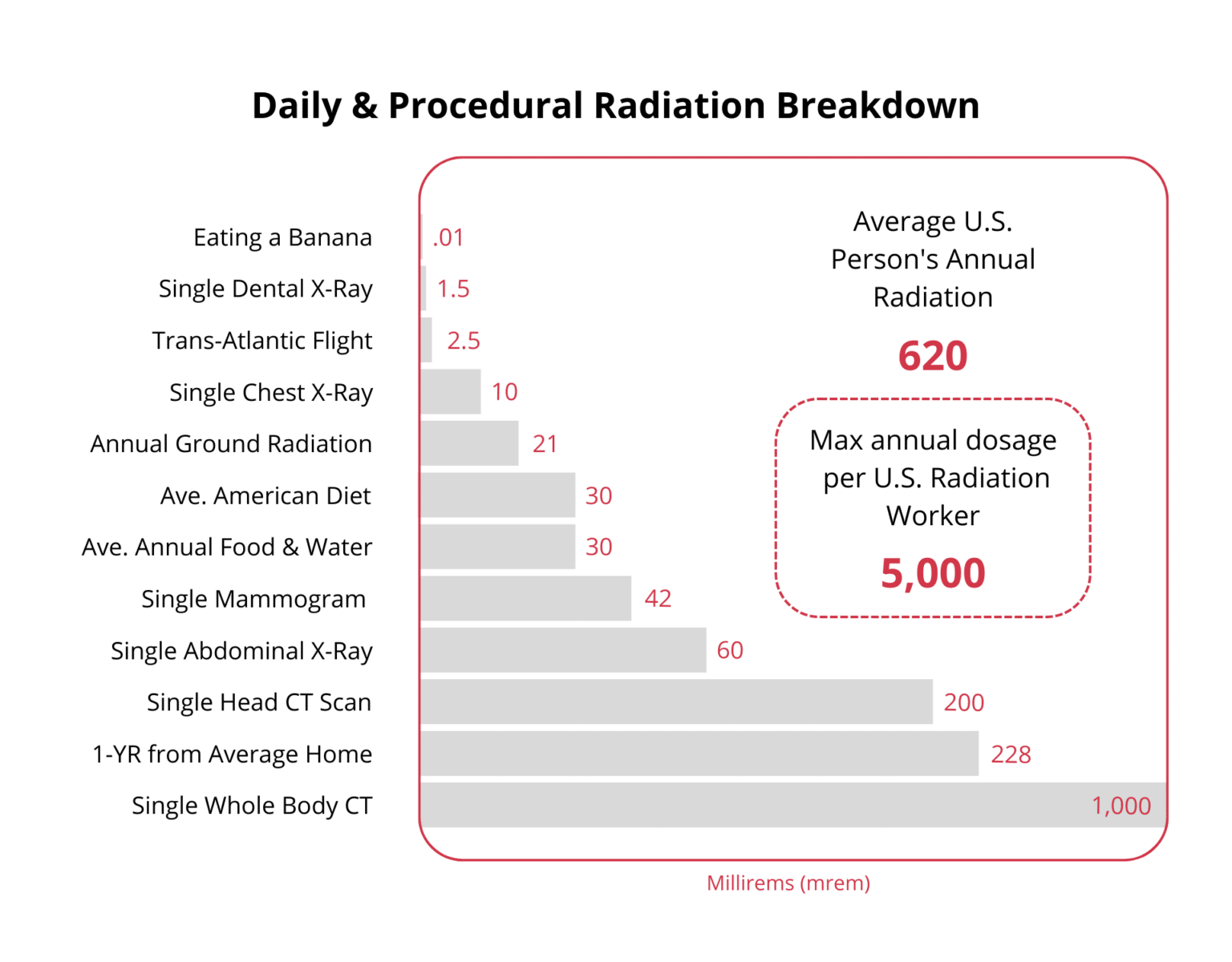
Dental X Ray Radiation Dose Chart - Web in figure 1, the dose from two intraoral films is 0.002 msv. This chart shows the amount of radiation a person receives from various activities. This chart shows the amount of radiation a person receives from various activities. Overall, 70.2% of all intraoral radiographs were dental, 20.3% bitewing and 9.5% occlusal radiographs. ─ infections that develop under your gums; This chart simplifies a highly complex topic for patients’ informational use. Web the national council on radiation protection and measurements (ncrp) has estimated that the mean effective radiation dose from all sources in the u.s. Web ─ caries (tooth decay) that develops between the teeth or under restorations (fillings); For occlusal radiographs, the dap was 7.43 cgy × cm 2 and the ed 2.22 µsv. Unnecessary radiation exposure to patients results when films need to be retaken due to faulty radiographic or processing techniques. Web comparison of the total effective dose (effective dose multiplied by the number of image sets) with that from other radiation sources: Digital intraoral sensors require less radiation dose than traditional film to produce an image. Web effective dose calculations based on the revised guidelines given by the international commission on radiological protection (icrp 103). ─ infections that develop under your gums; In fact, head and neck radiation treatment can increase the risk of developing tooth decay, making the radiographs all the more important for these patients. Dental radiographs can alert your dentist to changes in your hard and soft tissues. The biggest beer gut in the world isn’t 1,000 times the width of the cheek and gums. Web because of the low radiation dose associated with dental radiographs, people who have received radiation treatment for head and neck cancer can undergo dental radiography safely. An expert panel presents recommendations on radiation safety, appropriate imaging practices, and reducing radiation exposure. Overall, 70.2% of all intraoral radiographs were dental, 20.3% bitewing and 9.5% occlusal radiographs. For occlusal radiographs, the dap was 7.43 cgy × cm 2 and the ed 2.22 µsv. ─ infections that develop under your gums; Web typical effective doses are for: This chart shows the amount of radiation a person receives from various activities. This chart shows the amount of radiation a person receives from various activities. Airplane flight from ny to los angeles: This chart simplifies a highly complex topic for patients’ informational use. Radiation workers 50.00000 whole body ct scan 10.00000 Web comparison of the total effective dose (effective dose multiplied by the number of image sets) with that from other radiation sources: Web because of the low radiation dose associated with dental radiographs, people. Additional yearly dose to aircrew members: Digital intraoral sensors require less radiation dose than traditional film to produce an image. ─ diseases in the bone; Effective dose measured in microsieverts (μsv) describes the effect on the body’s various tissues when exposed by radiation from various sources. That’s more than 1,000 times more radiation dose to the lower back than to. Web • going through an airport security scanner 80 times is the equivalent to a single day of casual radiation exposure. ─ diseases in the bone; Radiation workers 50 whole body. Radiation workers 50.00000 whole body ct scan 10.00000 Web ─ caries (tooth decay) that develops between the teeth or under restorations (fillings); ─ some types of tumors. The biggest beer gut in the world isn’t 1,000 times the width of the cheek and gums. Additional yearly dose to aircrew members: Effective dose measured in microsieverts (μsv) describes the effect on the body’s various tissues when exposed by radiation from various sources. Web ─ caries (tooth decay) that develops between the teeth or. Additional yearly dose to aircrew members: Web here are some approximate comparisons of background radiation and effective radiation dose in adults for several radiology procedures described on this website. Web normal daily background dose for an average person: An expert panel presents recommendations on radiation safety, appropriate imaging practices, and reducing radiation exposure. These values can vary greatly, depending on. An expert panel presents recommendations on radiation safety, appropriate imaging practices, and reducing radiation exposure. This chart shows the amount of radiation a person receives from various activities. Web in figure 1, the dose from two intraoral films is 0.002 msv. Web effective dose calculations based on the revised guidelines given by the international commission on radiological protection (icrp 103).. The biggest beer gut in the world isn’t 1,000 times the width of the cheek and gums. That’s more than 1,000 times more radiation dose to the lower back than to the mouth. Additional yearly dose to aircrew members: This chart shows the amount of radiation a person receives from various activities. Web typical effective doses are for: Web typical effective doses are for: These values can vary greatly, depending on the size of the patient and the type of. This chart shows the amount of radiation a person receives from various activities. For occlusal radiographs, the dap was 7.43 cgy × cm 2 and the ed 2.22 µsv. Web because of the low radiation dose associated with. Radiation source dosage (msv) max annual dose permitted for u.s. Effective dose measured in microsieverts (μsv) describes the effect on the body’s various tissues when exposed by radiation from various sources. Unnecessary radiation exposure to patients results when films need to be retaken due to faulty radiographic or processing techniques. The actual dose can vary substantially, depending on a person’s. In fact, head and neck radiation treatment can increase the risk of developing tooth decay, making the radiographs all the more important for these patients. Airplane flight from ny to los angeles: ─ some types of tumors. An expert panel presents recommendations on radiation safety, appropriate imaging practices, and reducing radiation exposure. Radiation workers 50 whole body. This chart shows the amount of radiation a person receives from various activities. For occlusal radiographs, the dap was 7.43 cgy × cm 2 and the ed 2.22 µsv. Radiation workers 50.00000 whole body ct scan 10.00000 Effective dose measured in microsieverts (μsv) describes the effect on the body’s various tissues when exposed by radiation from various sources. ─ infections that develop under your gums; Web because of the low radiation dose associated with dental radiographs, people who have received radiation treatment for head and neck cancer can undergo dental radiography safely. Radiation source dose equivalent (msv) max annual dose permitted for u.s. Web comparison of the total effective dose (effective dose multiplied by the number of image sets) with that from other radiation sources: Unnecessary radiation exposure to patients results when films need to be retaken due to faulty radiographic or processing techniques. Web in figure 1, the dose from two intraoral films is 0.002 msv. These values can vary greatly, depending on the size of the patient and the type of.ficat grad atârna dental x ray radiation dose chart Legitim
Dental x ray radiation dose chart berylogin
XRay Safety Review Wexford Orthodontics
Are Dental Xrays Safe? Plaza Dental
Radiation Dosage Chart Information Is Beautiful Dental facts
Hannon & Sandler Dentistry
Dental X Ray Radiation Chart
Dental Radiation Dose Chart
How often should you get dental x rays? Beverly Hills Dentists
Are Dental XRays Safe? BDG
Web For Dental And Bitewing Radiographs, The Dose Area Product (Dap) Was 2.57 Cgy × Cm 2 And The Effective Dose (Ed) 0.77 Μsv.
Digital Intraoral Sensors Require Less Radiation Dose Than Traditional Film To Produce An Image.
Web The National Council On Radiation Protection And Measurements (Ncrp) Has Estimated That The Mean Effective Radiation Dose From All Sources In The U.s.
The Biggest Beer Gut In The World Isn’t 1,000 Times The Width Of The Cheek And Gums.
Related Post: