Endometrial Polyp Size Chart
Endometrial Polyp Size Chart - Web endometrial polyps refer to overgrowths of endometrial glands and stroma within the uterine cavity. Polyps may be found as a single lesion or multiple lesions filling the entire endometrial cavity. They also range in number women can have one or many endometrial polyps. Web uterine polyps, also known as endometrial polyps, form as a result of cells in the lining of the uterus (endometrium) overgrowing. These polyps are usually noncancerous (benign), although some can be cancerous or can turn into cancer (precancerous polyps). You may have one or several polyps present. Endometrial polyps vary in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. Web an endometrial polyp or uterine polyp is a mass in the inner lining of the uterus. Transvaginal ultrasonography (tvus) should be the imaging modality of choice for the detection of endometrial polyps in woman of fertile age (level b). Unlike polyps of other etiologies (eg, colon), the vast majority of endometrial polyps are neither malignant nor premalignant. Web an endometrial polyp or uterine polyp is an abnormal growth containing glands, stroma and blood vessels projecting from the lining of the uterus (endometrium) that occupies spaces small or large enough to fill the uterine cavity. Abnormal cell changes are often associated with malignancy, but the vast. Polyps may be found as a single lesion or multiple lesions filling the entire endometrial cavity. Polyps may be round or oval and range in size from a few millimeters (the size of a sesame seed) to a few centimeters (the size of a golf ball) or larger. Web uterine polyps, also known as endometrial polyps, form as a result of cells in the lining of the uterus (endometrium) overgrowing. Endometrial polyps vary in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. They range in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters. They may have a large flat base ( sessile) or be attached to the uterus by an elongated pedicle ( pedunculated ). You may have one or several polyps present. Web an endometrial polyp or uterine polyp is a mass in the inner lining of the uterus. They also range in number women can have one or many endometrial polyps. Polyps may be round or oval and range in size from a few millimeters (the size of a sesame seed) to a few centimeters (the size of a golf ball) or larger. You may have one or several polyps present. These polyps are usually noncancerous (benign), although. They contain glands, connective tissues, and blood vessels. Web the polyp attaches to the endometrium by a thin stalk or a broad base and extends into your uterus. Web an endometrial polyp or uterine polyp is an abnormal growth containing glands, stroma and blood vessels projecting from the lining of the uterus (endometrium) that occupies spaces small or large enough. Web an endometrial polyp or uterine polyp is a mass in the inner lining of the uterus. They also range in number women can have one or many endometrial polyps. Uterine polyps range in size from a few millimeters — no larger than a sesame seed. They contain glands, connective tissues, and blood vessels. Polyps may be round or oval. Web uterine polyps, also known as endometrial polyps, form as a result of cells in the lining of the uterus (endometrium) overgrowing. Polyps may be found as a single lesion or multiple lesions filling the entire endometrial cavity. [2] [3] pedunculated polyps are more common than sessile ones. Web endometrial polyps are one of the most common etiologies of abnormal. Web uterine polyps, also known as endometrial polyps, form as a result of cells in the lining of the uterus (endometrium) overgrowing. They contain glands, connective tissues, and blood vessels. Web an endometrial polyp or uterine polyp is an abnormal growth containing glands, stroma and blood vessels projecting from the lining of the uterus (endometrium) that occupies spaces small or. [2] [3] pedunculated polyps are more common than sessile ones. Polyps may be round or oval and range in size from a few millimeters (the size of a sesame seed) to a few centimeters (the size of a golf ball) or larger. Can range in size from millimeters (about the size of a sesame seed) to centimeters (about the size. Web endometrial polyps are one of the most common etiologies of abnormal genital tract bleeding in both premenopausal and postmenopausal patients ( table 1 ). They contain glands, connective tissues, and blood vessels. You may have one or several polyps present. Abnormal cell changes are often associated with malignancy, but the vast. They may have a large flat base (. Unlike polyps of other etiologies (eg, colon), the vast majority of endometrial polyps are neither malignant nor premalignant. Web endometrial polyps are caused by the overgrowth of endometrial tissue, which is the lining of the uterus that swells and then shrinks during the menstrual cycle. Transvaginal ultrasonography (tvus) should be the imaging modality of choice for the detection of endometrial. Transvaginal ultrasonography (tvus) should be the imaging modality of choice for the detection of endometrial polyps in woman of fertile age (level b). Endometrial polyps vary in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. They contain glands, connective tissues, and blood vessels. Web the polyp attaches to the endometrium by a thin stalk or a broad base. Transvaginal ultrasonography (tvus) should be the imaging modality of choice for the detection of endometrial polyps in woman of fertile age (level b). You may have one or several polyps present. Web the polyp attaches to the endometrium by a thin stalk or a broad base and extends into your uterus. Abnormal cell changes are often associated with malignancy, but. Endometrial polyps vary in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters in diameter. Web uterine polyps, also known as endometrial polyps, form as a result of cells in the lining of the uterus (endometrium) overgrowing. Polyps may be found as a single lesion or multiple lesions filling the entire endometrial cavity. Can range in size from millimeters (about the size of a sesame seed) to centimeters (about the size of a golf ball and even larger). Web an endometrial polyp or uterine polyp is an abnormal growth containing glands, stroma and blood vessels projecting from the lining of the uterus (endometrium) that occupies spaces small or large enough to fill the uterine cavity. Abnormal cell changes are often associated with malignancy, but the vast. Web the polyp attaches to the endometrium by a thin stalk or a broad base and extends into your uterus. Transvaginal ultrasonography (tvus) should be the imaging modality of choice for the detection of endometrial polyps in woman of fertile age (level b). They also range in number women can have one or many endometrial polyps. Uterine polyps range in size from a few millimeters — no larger than a sesame seed. Polyps may be round or oval and range in size from a few millimeters (the size of a sesame seed) to a few centimeters (the size of a golf ball) or larger. Web endometrial polyps are one of the most common etiologies of abnormal genital tract bleeding in both premenopausal and postmenopausal patients ( table 1 ). These polyps are usually noncancerous (benign), although some can be cancerous or can turn into cancer (precancerous polyps). They contain glands, connective tissues, and blood vessels. Web endometrial polyps are caused by the overgrowth of endometrial tissue, which is the lining of the uterus that swells and then shrinks during the menstrual cycle. Web endometrial polyps form from an overgrowth of cells within the uterine lining.Endometrial Polyp Size Chart
Endometrial Polyp Size Chart In Mm
Dra. Joana Faria Uterine polyp Lisbon, Portugal
[PDF] Giant endometrial polyp protruding from the external cervical os
Uterine Polyp Size Chart
Representative size measurement and appearance of endometrial polyps
Uterine Polyp Size Chart
Endometrial Polyp Size Chart In Mm
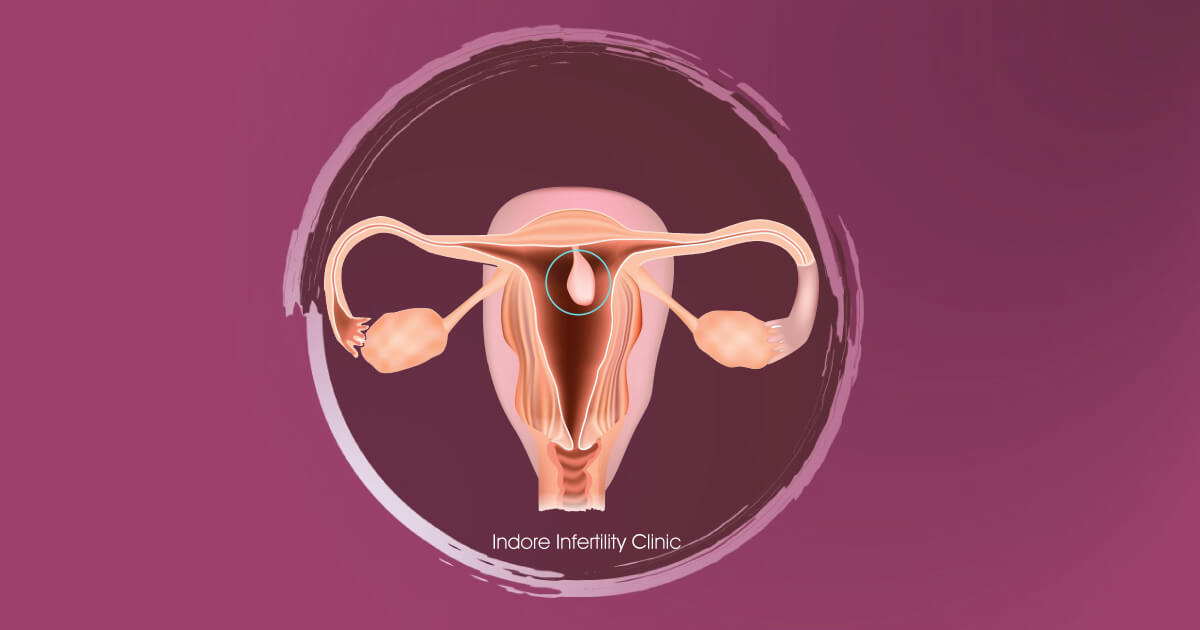
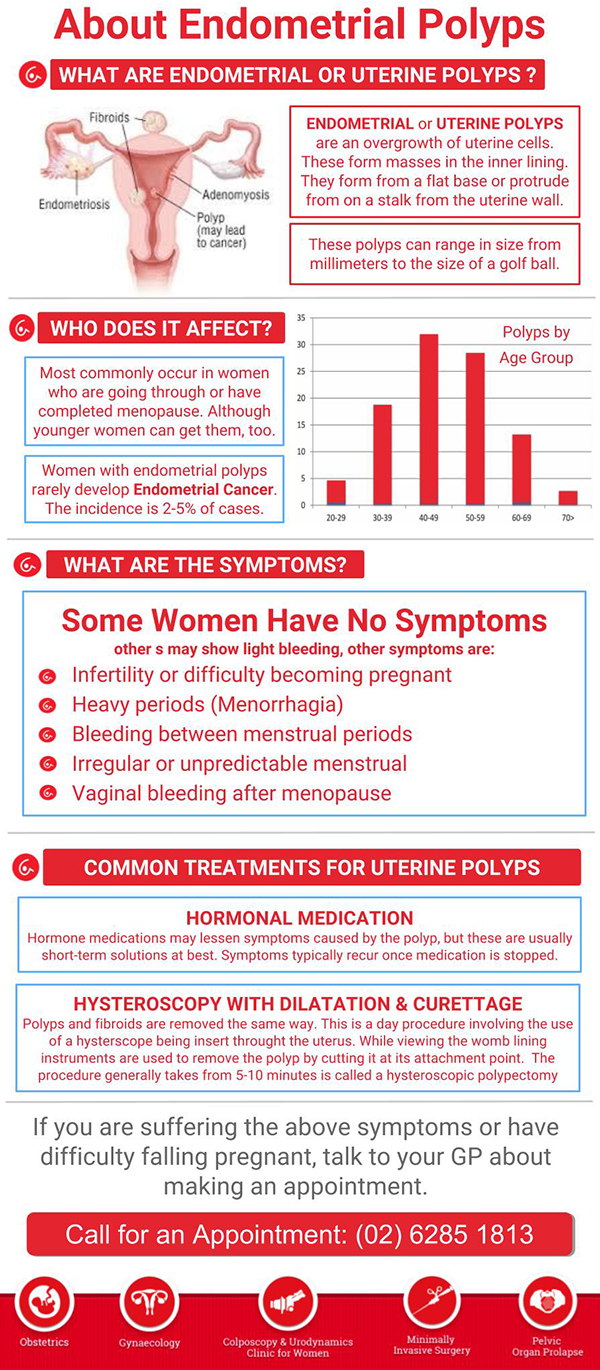
Endometrial & Uterine Polyps Canberra Deakin, ACT
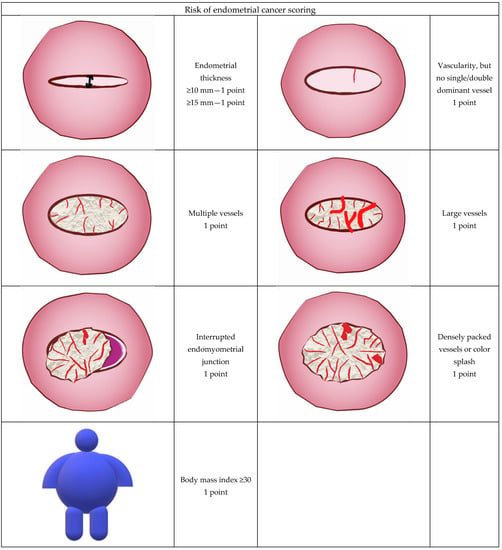
Diagnostics Free FullText Risk Assessment of Endometrial
Unlike Polyps Of Other Etiologies (Eg, Colon), The Vast Majority Of Endometrial Polyps Are Neither Malignant Nor Premalignant.
Web Endometrial Polyps Refer To Overgrowths Of Endometrial Glands And Stroma Within The Uterine Cavity.
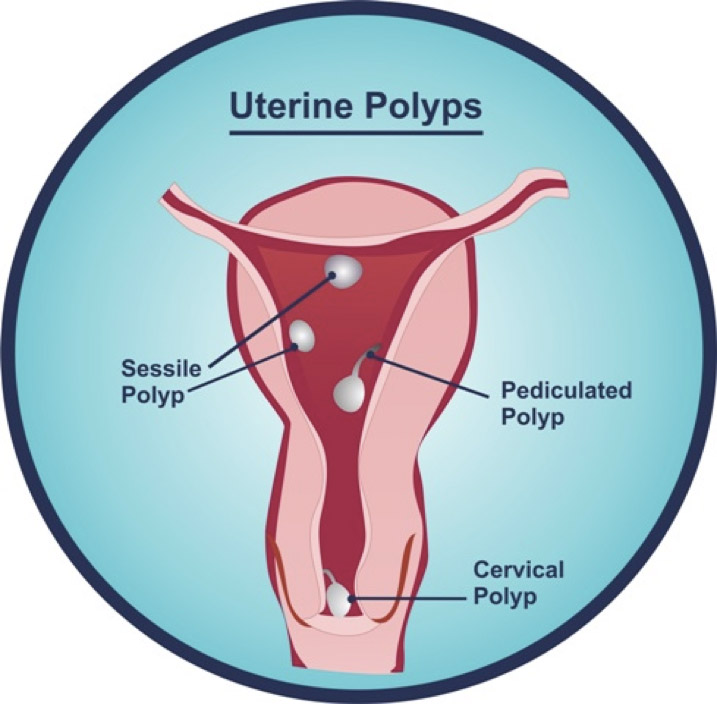
[2] [3] Pedunculated Polyps Are More Common Than Sessile Ones.
They Range In Size From A Few Millimeters To Several Centimeters.
Related Post:
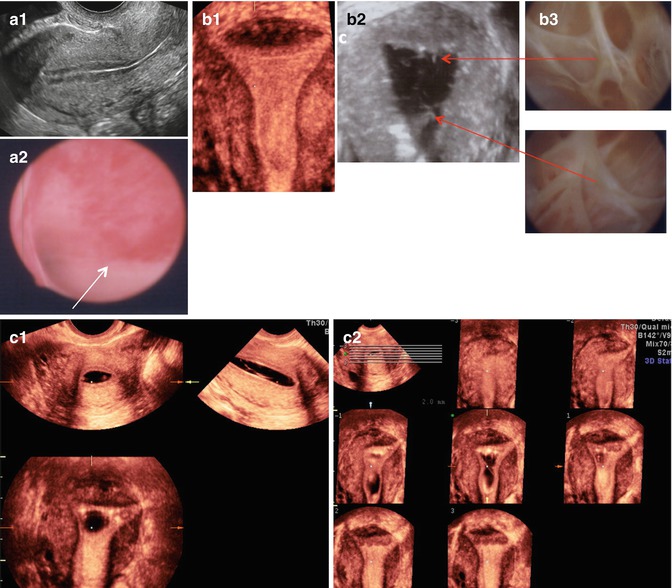

![[PDF] Giant endometrial polyp protruding from the external cervical os](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/8ee776e2c239fe8f6fe5bef07581c99c4de87bae/5-Figure4-1.png)