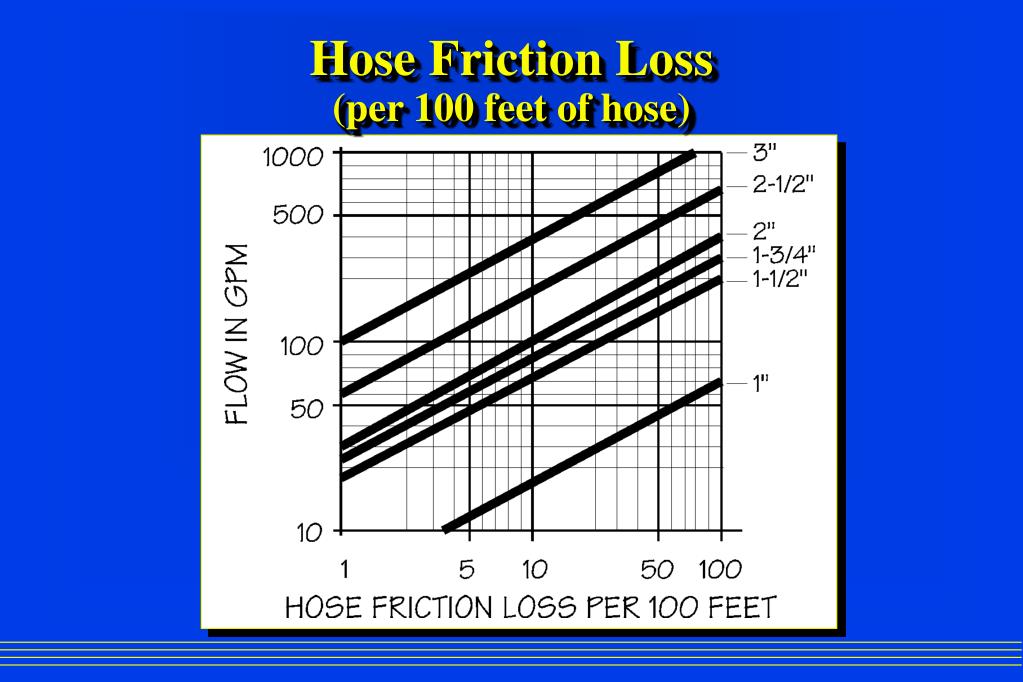
Friction Loss Fire Hose Chart
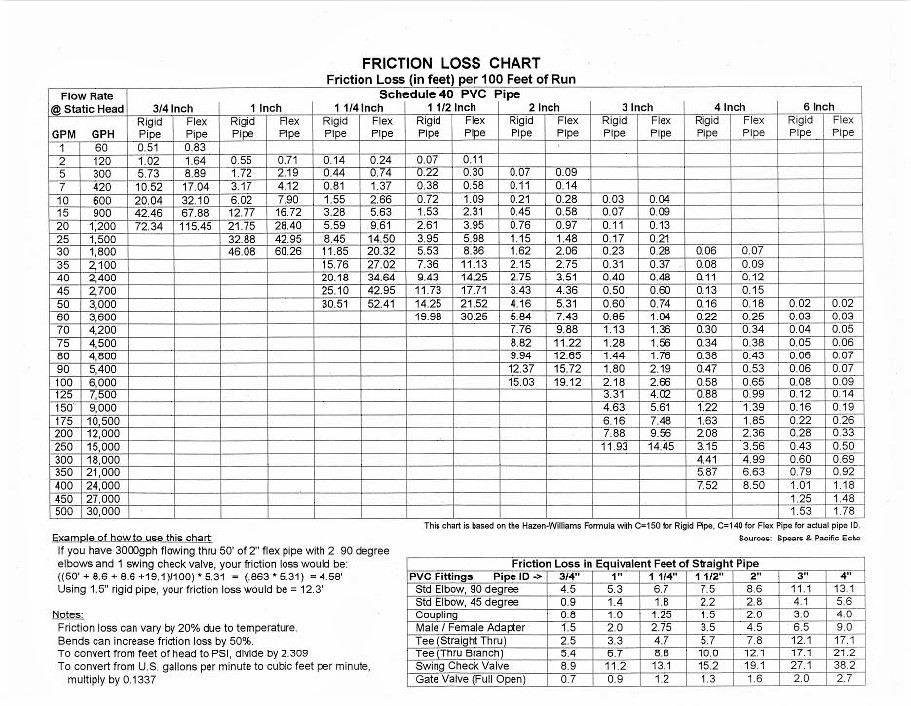
Friction Loss Fire Hose Chart - These calculations are meant to be a guideline. From fire hose to foam equipment, no other manufacturer offers a more complete solution. Web friction losses on reeled hose average about 21 percent more than for straight hose lays. Web you can access fire hose friction loss charts or cheat sheets⁵ for the most common hose sizes. Numbers in blue for nozzle at standard 100 psi setting numbers in red for nozzle at low pressure setting There is no set friction loss for any one size of hose. The charts were developed by applying friction loss formulas or by testing the department’s. Web most fire departments calculate the friction loss for the hoses and nozzles they carry and write them on what is called a “pump chart.” most charts list the nozzles on the apparatus,. Web the first method for determining friction loss is to use a pump chart, as do most fire departments. Choose your hose and size below, enter the flow rate, as well as the hose length to display friction loss data. Friction loss varies with type, lining, weave, quality, and age of the hose. Web friction loss iii fire hose loss in psi per 100 feet of hose size hose linen hose best ruber lined. Numbers in blue for nozzle at standard 100 psi setting numbers in red for nozzle at low pressure setting Friction loss increases 4 times for each doubling of water flow. Web a fire friction loss calculator is a valuable tool that helps firefighters determine the pressure drop in a fire hose due to friction, enabling them to select the appropriate hose size and pump pressure for effective firefighting operations. Web enter the hose diameter, the gallons per minute (gpm), and the length, into the friction loss calculator Friction loss will vary based on hose manufacturer. Choose your hose and size below, enter the flow rate, as well as the hose length to display friction loss data. Pressure loss per 100 feet (psi) These calculations are meant to be a guideline. Friction loss increases 4 times for each doubling of water flow. Web friction loss per 100 feet of hose line. Friction loss varies with type, lining, weave, quality, and age of the hose. The charts were developed by applying friction loss formulas or by testing the department’s. From fire hose to foam equipment, no other manufacturer offers a more complete. This number affects the pump discharge pressure needed to achieve your desired flow rate. Web enter the hose diameter, the gallons per minute (gpm), and the length, into the friction loss calculator Web all fire hose has friction loss. Web (2) friction loss may vary with brand and condition of hose. Web most fire departments calculate the friction loss for. Choose your hose and size below, enter the flow rate, as well as the hose length to display friction loss data. Click the link to see our friction loss data. Web study has been to develop baseline friction loss coefficients for the types of fire hose commonly used by today’s fire service, and identify any additional performance characteristics that should. Web the first method for determining friction loss is to use a pump chart, as do most fire departments. This number affects the pump discharge pressure needed to achieve your desired flow rate. Web you can access fire hose friction loss charts or cheat sheets⁵ for the most common hose sizes. Web most fire departments calculate the friction loss for. Please click on the table above to. Web just what you need to calculate the most precise friction loss for a wide range of key hose products. This number affects the pump discharge pressure needed to achieve your desired flow rate. There is no set friction loss for any one size of hose. From fire hose to foam equipment, no. Web the kuriyama fire products friction loss calculator provides accurate friction loss for our hose. Web just what you need to calculate the most precise friction loss for a wide range of key hose products. Pressure loss per 100 feet (psi) Web loss in fire hose. Please click on the table above to. These calculations are meant to be a guideline. Web the friction loss sheet allows you to input gpm, pump discharge pressure, desired nozzle pressure, and elevation change and it will calculate the length of hose using both standard c values. Web enter the hose diameter, the gallons per minute (gpm), and the length, into the friction loss calculator Choose your. Web study has been to develop baseline friction loss coefficients for the types of fire hose commonly used by today’s fire service, and identify any additional performance characteristics that should be considered for friction loss calculations. Numbers in blue for nozzle at standard 100 psi setting numbers in red for nozzle at low pressure setting Web friction loss per 100. Web friction loss iii fire hose loss in psi per 100 feet of hose size hose linen hose best ruber lined. Please click on the table above to. Web the friction loss formula allows you to calculate the friction loss you experience from the pump to the nozzle. Web you can access fire hose friction loss charts or cheat sheets⁵. Web most fire departments calculate the friction loss for the hoses and nozzles they carry and write them on what is called a “pump chart.” most charts list the nozzles on the apparatus,. Web enhance firefighting efficiency with the friction loss calculator, offering precision tools for hose performance optimization. This number affects the pump discharge pressure needed to achieve your. Friction loss varies with type, lining, weave, quality, and age of the hose. Friction loss increases 4 times for each doubling of water flow. Click the link to see our friction loss data. Friction loss is determined by the gpm flowing, the size of the hose and the length of. Web (2) friction loss may vary with brand and condition of hose. These will give you the fl for a certain gpm measurement, which you can then use in calculating pump discharge pressure. Web enter the hose diameter, the gallons per minute (gpm), and the length, into the friction loss calculator and then press the submit button. Web the friction loss formula allows you to calculate the friction loss you experience from the pump to the nozzle. Web the first method for determining friction loss is to use a pump chart, as do most fire departments. Numbers in blue for nozzle at standard 100 psi setting numbers in red for nozzle at low pressure setting Web all fire hose has friction loss. Web friction losses on reeled hose average about 21 percent more than for straight hose lays. Losses in rough walled, rubber hose may be 50% higher than values given above. Pressure loss per 100 feet (psi) Friction loss is nearly independent of pressure. Choose your hose and size below, enter the flow rate, as well as the hose length to display friction loss data.Fire Hose Friction Loss Chart
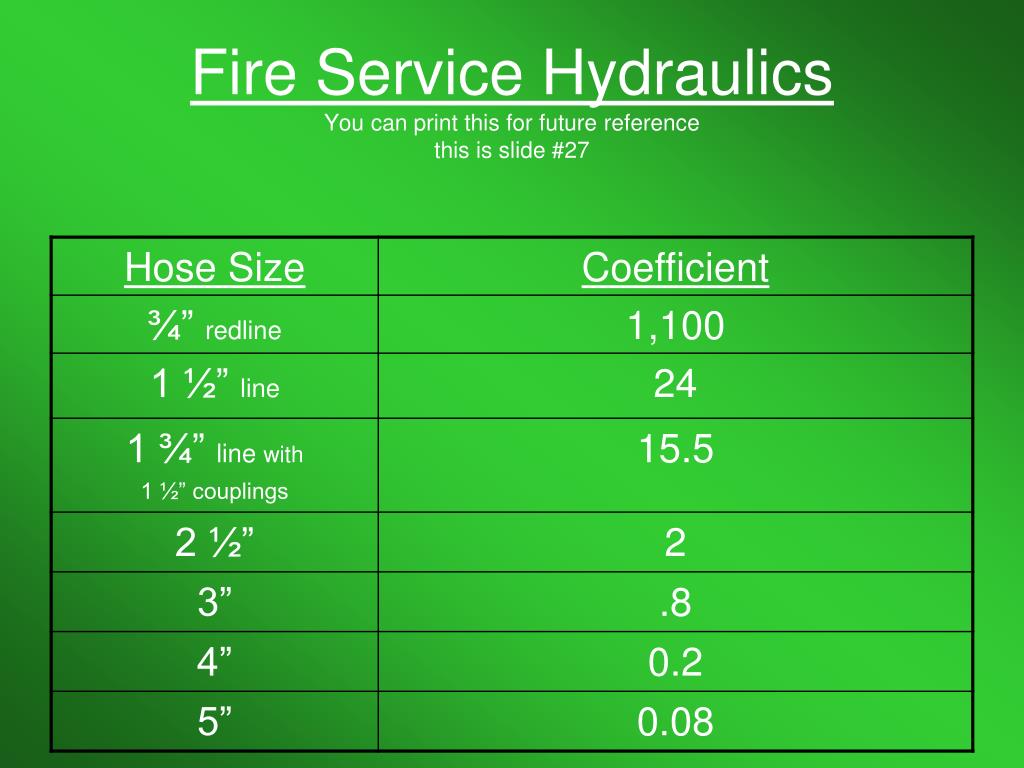
fire hose friction loss coefficient chart Focus
Fire Pump Friction Loss Cheat Sheet Chart
Fire Hose Friction Loss Coefficient Chart vrogue.co
Fire Hose Friction Loss Cheat Sheet Printable Templates Free
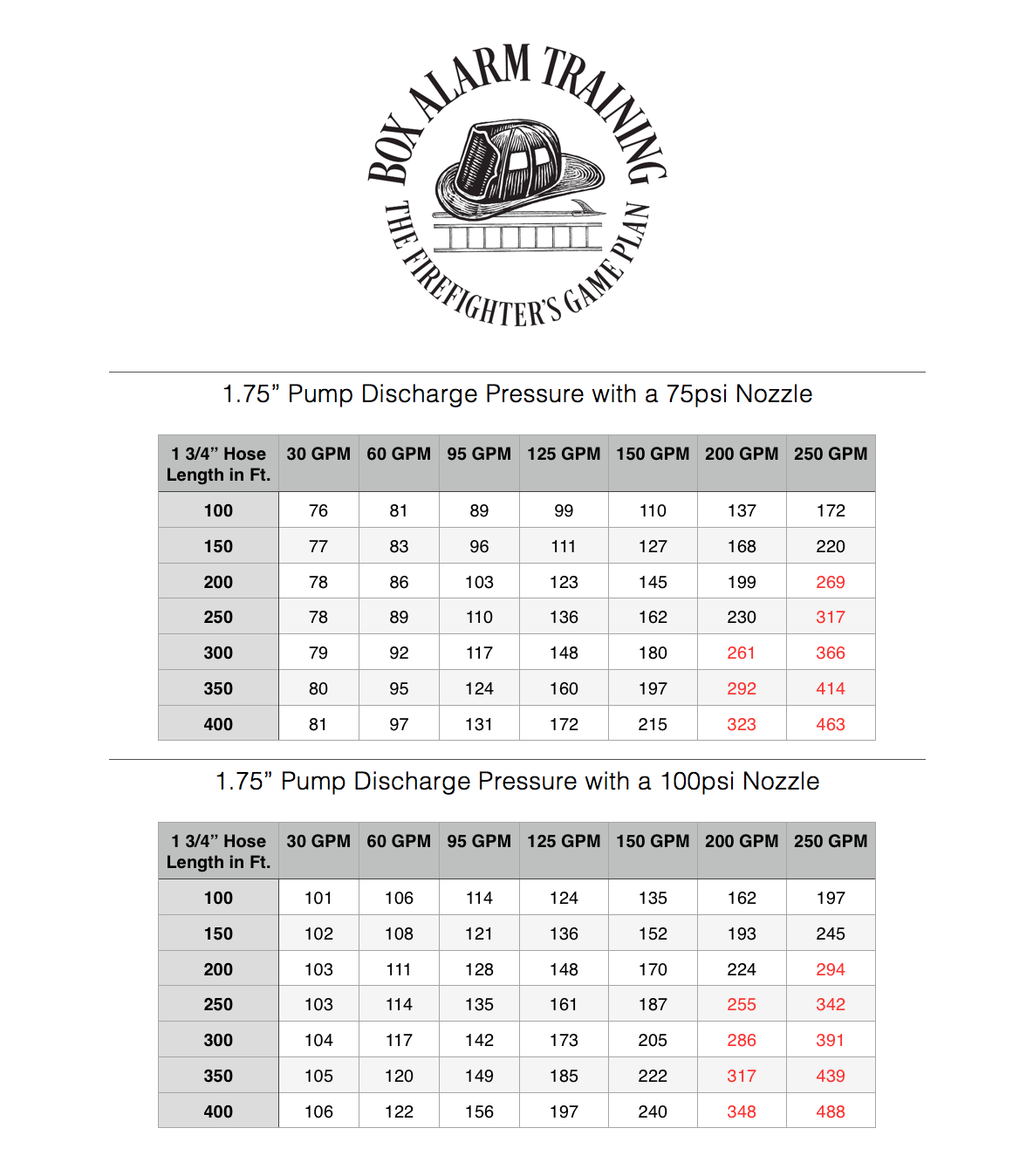
1.75 inch Friction Loss Calculator Fire training, Firefighter
Fire Hose Friction Loss Coefficient Chart
Fire Hose Friction Loss Cheat Sheet
Fire Hose Friction Loss Chart
Fire Hose Friction Loss Coefficient Chart
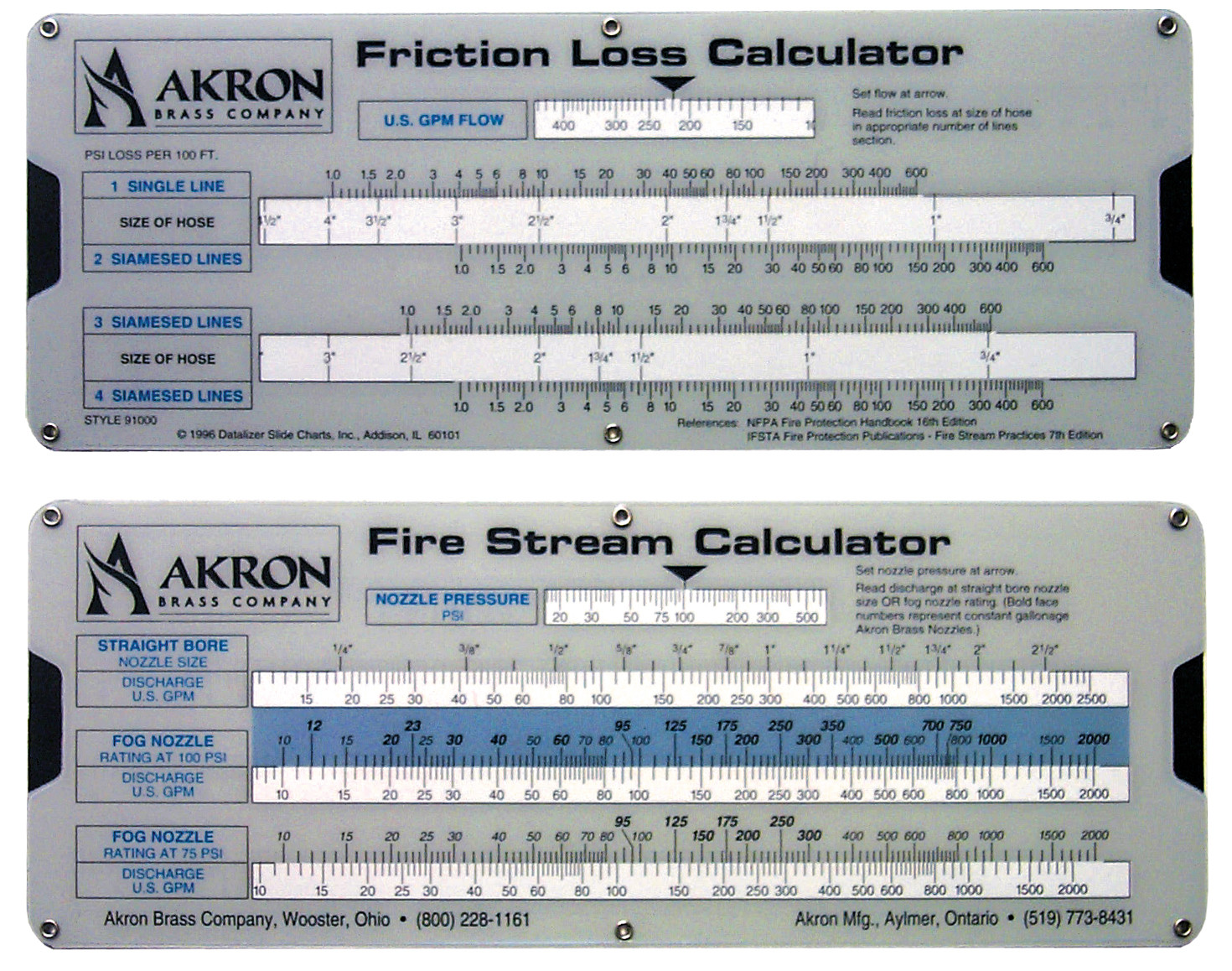
Web Just What You Need To Calculate The Most Precise Friction Loss For A Wide Range Of Key Hose Products.
There Is No Set Friction Loss For Any One Size Of Hose.
Web Friction Loss Per 100 Feet Of Hose Line.
From Fire Hose To Foam Equipment, No Other Manufacturer Offers A More Complete Solution.
Related Post: