Sediment Size Chart
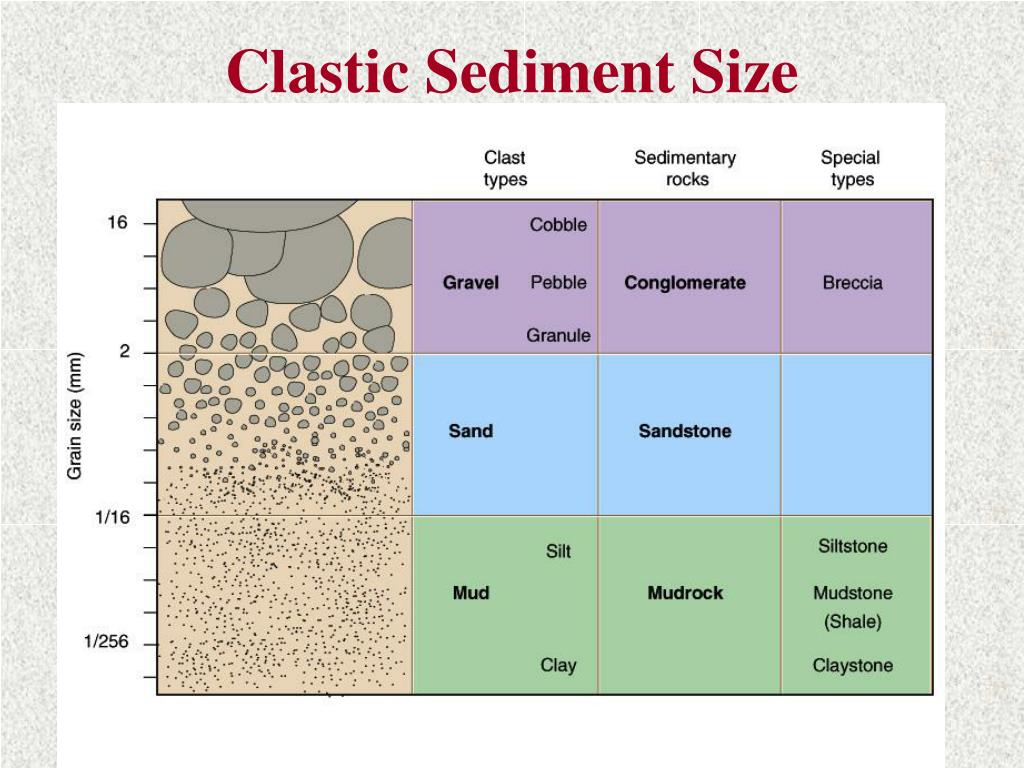
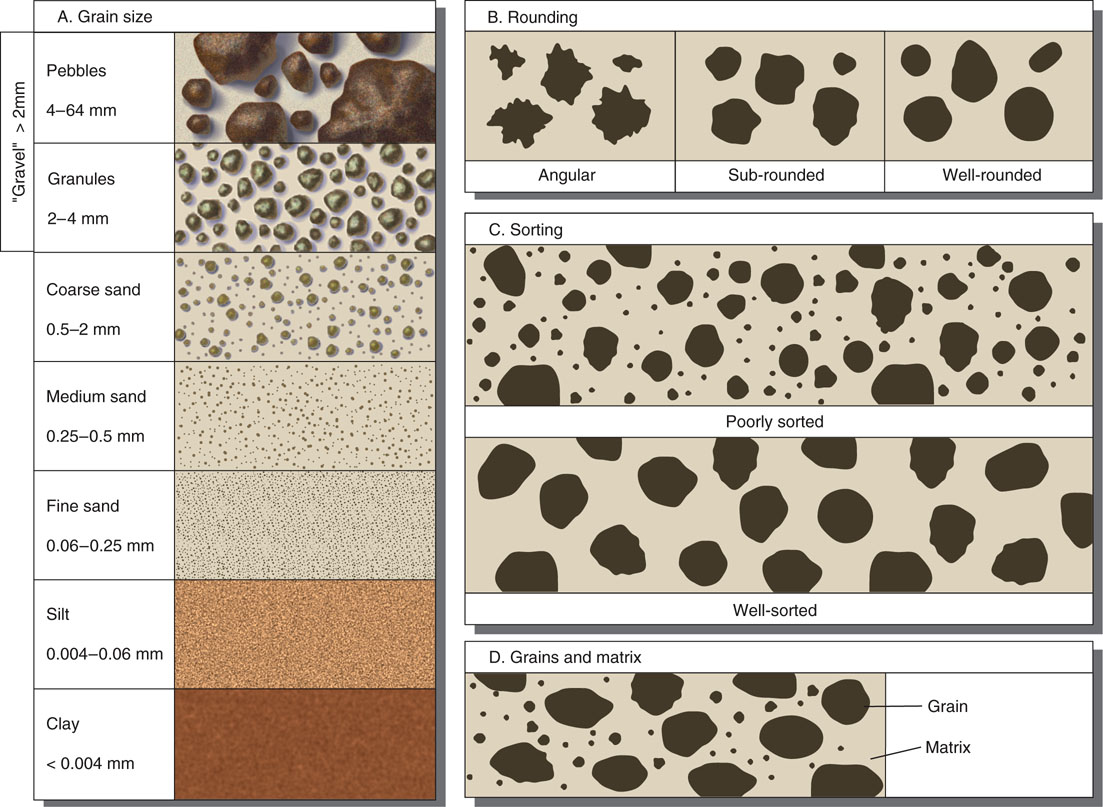
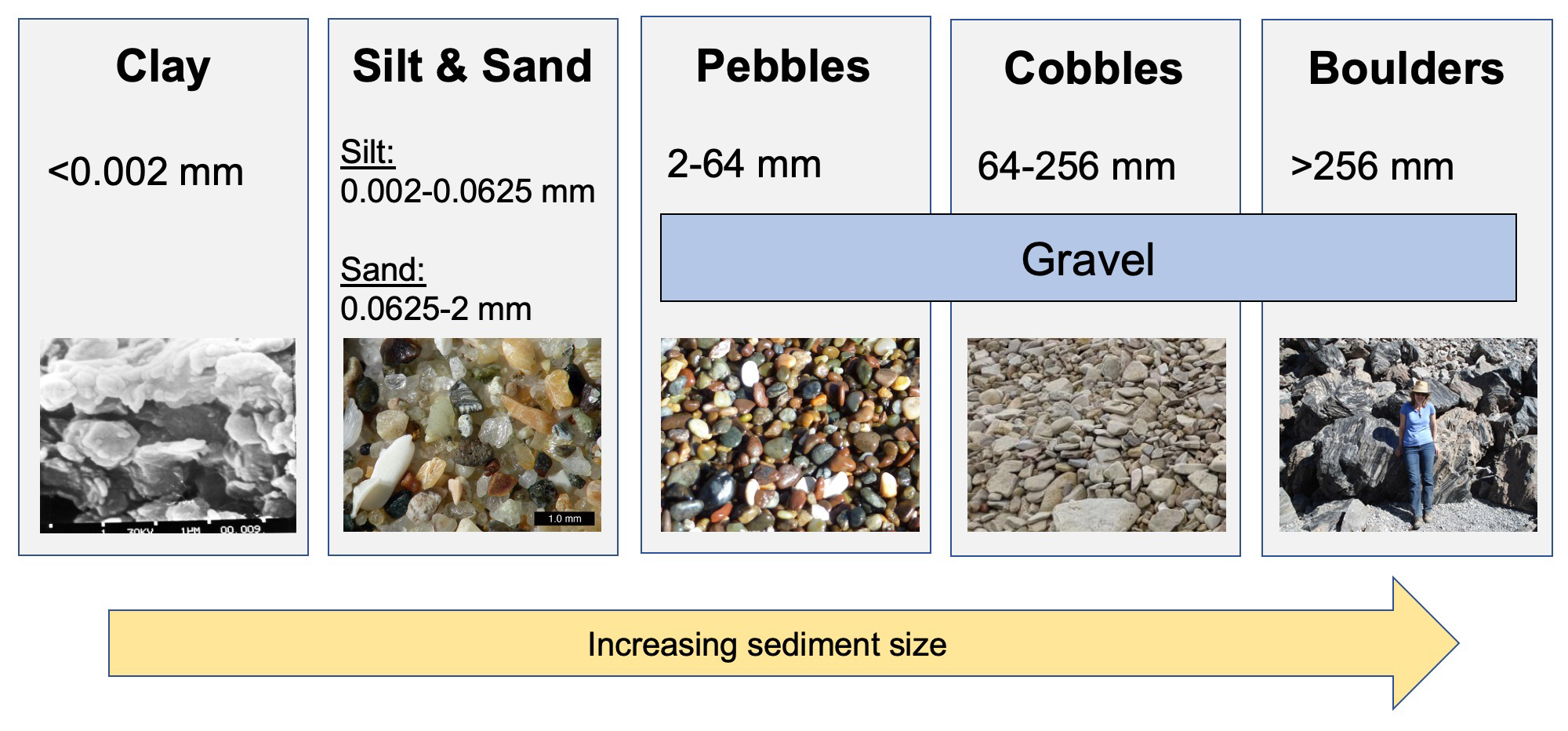
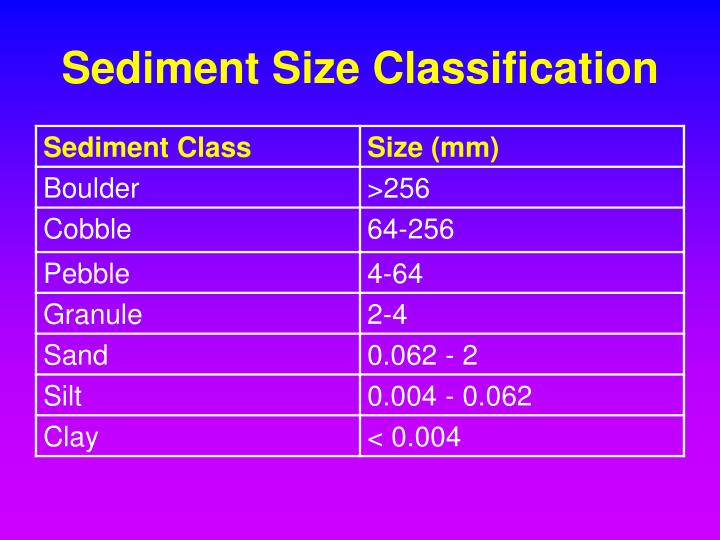
Sediment Size Chart - Particle size, also called grain size, refers to the diameter of individual grains of sediment, or the lithified particles in clastic rocks. A scale of grade and. The term may also be applied to other granular materials. Table adapted from the wentworth scale, wentworth, c.k. Grain size (or particle size) is the diameter of individual grains of sediment, or the lithified particles in clastic rocks. A single grain can be composed of several crystals. Web grain size scale, in sedimentology, division of a continuous range of particle sizes into a series of discrete groups. Web pettijohn (1975) has pointed out three types of size classification: Find out why grain size is important for. Describe grains using sorting and rounding. The term may also be applied to other granular materials. Web sieve analysis of sediment, log and histogram grain size plots, statistical measures of mean, mode, median, sorting, skewness. Web grain size scale, in sedimentology, division of a continuous range of particle sizes into a series of discrete groups. Convert between millimeters and phi units. Mean grain size of loose sediments is measured by size. Web however, beaches may be composed of sediments of various sizes: Web clastic sedimentary particles are most commonly classified by grain size (see sediment size classification). Learn how sediment grain size affects the formation of sedimentary rocks and how geologists measure it. Web there are a number of ways that we can classify ocean sediments, and some of the most common distinctions are based on the sediment texture, the sediment. Granular material can range from very small colloidal particles, through clay, silt, sand, gravel, and cobbles, to boulders. Web most sediments contain particles that have a range of sizes, so the mean or average grain size is used in description. Find out why grain size is important for. Web there are a number of ways that we can classify ocean sediments, and some of the most common distinctions are based on the sediment texture, the sediment. Use these. Particle size, also called grain size, refers to the diameter of individual grains of sediment, or the lithified particles in clastic rocks. A single grain can be composed of several crystals. The chart shows the different size fractions from silt (63 µm) through to large cobbles (128256 mm). Several such scales have been devised for the purpose of. Describe grains. Web clastic sedimentary particles are most commonly classified by grain size (see sediment size classification). (from finest to coarsest) mud (silt and clay), sand, and gravel (cobbles and boulders). Convert between millimeters and phi units. Diameter (mm) = 1/2 n. Several such scales have been devised for the purpose of. Web particle size (grain size) chart. Several such scales have been devised for the purpose of. (from finest to coarsest) mud (silt and clay), sand, and gravel (cobbles and boulders). Web the wentworth scale is a scale for classifying and describing sediments by grain size. The chart shows the different size fractions from silt (63 µm) through to large cobbles. Web traditionally, geologists have divided sediments into four size fractions that include gravel, sand, silt, and clay, and classified these sediments based on ratios of the various. This is different from the crystallite size, which refers to the size of a single crystal inside a particle or grain. Web there are a number of ways that we can classify ocean. (from finest to coarsest) mud (silt and clay), sand, and gravel (cobbles and boulders). A single grain can be composed of several crystals. Find out why grain size is important for. The chart shows the different size fractions from silt (63 µm) through to large cobbles (128256 mm). See a simplified version of the wentworth and phi scales for. Describe grains using sorting and rounding. Web the wentworth scale is a scale for classifying and describing sediments by grain size. Web grain size scale, in sedimentology, division of a continuous range of particle sizes into a series of discrete groups. Grain size (or particle size) is the diameter of individual grains of sediment, or the lithified particles in clastic. Web the wentworth scale is a scale for classifying and describing sediments by grain size. Web particle size (grain size) chart. Find out why grain size is important for. See a simplified version of the wentworth and phi scales for. Web sorting describes how fine to coarse grain sediments are distributed (settle), and how they will eventually lithify into sedimentary. Convert between millimeters and phi units. Several such scales have been devised for the purpose of. The chart shows the different size fractions from silt (63 µm) through to large cobbles (128256 mm). Find out why grain size is important for. Web there are a number of ways that we can classify ocean sediments, and some of the most common. Web the wentworth scale is a scale for classifying and describing sediments by grain size. Web in hydrogeology, we commonly describe sediment size in terms of phi units (φ), where the conversion to real world units is: Find out why grain size is important for. Sand and silt may be further modified by the terms (very). This is different from. Web most sediments contain particles that have a range of sizes, so the mean or average grain size is used in description. You can use them for hand specimens at home or in the classroom, or on rock outcrops. Web however, beaches may be composed of sediments of various sizes: See a simplified version of the wentworth and phi scales for. Grain size (or particle size) is the diameter of individual grains of sediment, or the lithified particles in clastic rocks. Table adapted from the wentworth scale, wentworth, c.k. Web traditionally, geologists have divided sediments into four size fractions that include gravel, sand, silt, and clay, and classified these sediments based on ratios of the various. Find out why grain size is important for. Web sieve analysis of sediment, log and histogram grain size plots, statistical measures of mean, mode, median, sorting, skewness. Sand and silt may be further modified by the terms (very). Use these grain size cards in your observations of sedimentary rocks. Web pettijohn (1975) has pointed out three types of size classification: Particle size, also called grain size, refers to the diameter of individual grains of sediment, or the lithified particles in clastic rocks. Mean grain size of loose sediments is measured by size. Learn how sediment grain size affects the formation of sedimentary rocks and how geologists measure it. Web particle size (grain size) chart.PPT Sediments and Sedimentary Rocks PowerPoint Presentation, free
Sediment grainsize scale Download Table
Sediment size scales and classes Download Table
Comparison of grain sizes to soils and loess sediment classification
Sediment Grain Size Chart
Sediment Grain Size Chart
Study Reveals How Climate Influences Sediment Size Geology In
Sediment size chart. Soil mechanics, Geology, Sedimentary rocks
Illustration Of The Four Levels In Sedimentary Hierarchy
PPT Sea Floor Sediments PowerPoint Presentation ID4654426
Granular Material Can Range From Very Small Colloidal Particles, Through Clay, Silt, Sand, Gravel, And Cobbles, To Boulders.
Web Clastic Sedimentary Particles Are Most Commonly Classified By Grain Size (See Sediment Size Classification).
Convert Between Millimeters And Phi Units.
Web The Wentworth Scale Is A Scale For Classifying And Describing Sediments By Grain Size.
Related Post: